[P1222] 三角形
Foxtr0t
·
·
题解
原题目
[P1222] 三角形
解析
很多人可能第一次就想到了水平/竖直扫描
于是给三角形排序,然后依次判断步长和上下底长
但是,原题给出的样例很有误导性,如果照着那个debug,那么。。。
我当时用了 3 小时找错误原因,测试了不同样例
自己测试永远都是 AC ,上传编译永远有 WA
废话好多呜呜,实现在最后
### 醒悟
最终我回看实现参考的原理:扫描端点判断步长,而不是每个重叠层数变化点
所以两种扫描方向都会出问题。。。
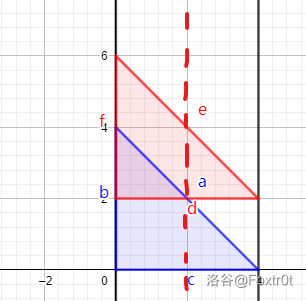
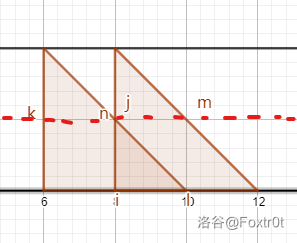
不止需要判断『端点』,还需要判断『「斜边」与「平行于扫描方向的腰」的交点』
属实离谱,有点难受,因为这样要改的太多了,还可能 TLE
为了挽救我的脑细胞,我做了一个违背初心的决定。。。
### 重启
对题目进行二次分析,发现:
主要矛盾是「对交点判定的需要」和「交点判定方法实现的困难」之间的矛盾
于是进行一个矛盾的转化:
```constexpr int step = 1;```
现在不会漏掉任何一点了,不管什么点都不会漏了!!!
但是会TLE,因为没有三角形的地方浪费了太多时间。。。
### 进化
主要矛盾转变为「三角形间隔之远」和「在间隔处走得太慢」之间的矛盾
虽然修 $bug * 1$ 获得 $bug * 99$ 但是现在的 $bug$ 很容易解决了
如果当前位置没有有效三角形就直接跳到下一个三角形
然后就可以美滋滋 AC 100
## 可能遇到的 issue
不开 O2 总会倒数第二 TLE —— 不要用 ```float``` ```double```,看上方『解析』 $ΔS$ 公式
和第一张图错误一样 —— 从头仔细看一下我的『解析』吧,这个问题是重点讲的
## 实现
按照这个思路的实现方法有很多种,太多种
下面提供一种我的 C++ 14 无 O2 代码
用了很多 ```std``` 的轮子,代码比较阴间,我尽力注释了
有意见或疑问欢迎评论区提 issue
```cpp
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
struct Triangle {
int x, y, m, x1, y1;
constexpr Triangle(int x_, int y_, int m_) : x(x_), y(y_), m(m_), x1(x_ + m_), y1(y_ + m_) {}
constexpr bool operator<(const Triangle& e) const { return (x < e.x) || (x == e.x) && (y < e.y); }
constexpr int height(int x_) const { return (x_ < x) ? 0 : x_ >= x1 ? 0 : (m + x - x_); }
constexpr int height1(int x_) const { return (x_ <= x) ? 0 : x_ >= x1 ? 0 : (m + x - x_); }
};
struct Section {
int a, b;
constexpr Section(int a_, int b_) : a(a_), b(b_) {}
constexpr bool operator<(const Section& e) const { return (a < e.a) || (a == e.a) && (b > e.b); }
constexpr operator int() const { return b - a; }
};
std::vector<Triangle> tri;
std::vector<Triangle> ctx;
int main() {
int n, x, _x, _y, _m, S = 0, loop = 1;
std::cin >> n;
while (n-- && ((std::cin >> _x >> _y >> _m), 1)) tri.emplace_back(_x, _y, _m); // read 三角形
std::sort(tri.begin(), tri.end()); // sort 三角形
x = tri[0].x; // first 三角形
for (size_t i = 0; i < tri.size(); i++)
{
ctx.emplace_back(tri[i]);
while (!(ctx.end()[-1].x == x && i + 1 < tri.size()))
{
int x1 = x + 1, h1 = 0;
std::vector<Section> section;
for (const auto& e : ctx)
if (Section tmp = { e.y, e.y + e.height(x) })
section.emplace_back(tmp); // push 有效区间
std::sort(section.begin(), section.end());
for (size_t i = 0; i + 1 < section.size(); i++)
while (loop++) // 区间合并 ++ 是在复位之前 判断是否继续循环
{
loop = 0;
while (i + 1 < section.size() && section[i].a == section[i + 1].a) section.erase(section.begin() + i + 1), loop = 1;
while (i + 1 < section.size() && section[i].b > section[i + 1].a) section[i].b = std::max(section[i].b, section[i + 1].b), section.erase(section.begin() + i + 1), loop = 1;
}
for (const auto& e : section)
{
S += 2ull * e - x1 + x; // S += (左底 + 右底) * 1 //* 0.5
h1 = h1 + e - x1 + x; // 右底
}
x = x1; // x++
if (!h1)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < ctx.size(); i++)
if (ctx[i].x1 <= x)
ctx.erase(ctx.begin() + i--); // TODO(可优化,内存复制浪费时间) // 移除失活三角形
if (!ctx.size())
break;
x = ctx[0].x; // 跳到下一个三角形
}
}
}
return printf("%d.%01d", S / 2, 5 * (S % 2)), 0; // S *= 0.5
}
```