AT_abc395_e [ABC395E] Flip Edge
Description
You are given a directed graph with $ N $ vertices and $ M $ edges. The $ i $ -th edge $ (1 \leq i \leq M) $ is a directed edge from vertex $ u _ i $ to vertex $ v _ i $ .
Initially, you are at vertex $ 1 $ . You want to repeat the following operations until you reach vertex $ N $ :
- Perform one of the two operations below:
- Move along a directed edge from your current vertex. This incurs a cost of $ 1 $ . More precisely, if you are at vertex $ v $ , choose a vertex $ u $ such that there is a directed edge from $ v $ to $ u $ , and move to vertex $ u $ .
- Reverse the direction of all edges. This incurs a cost of $ X $ . More precisely, if and only if there was a directed edge from $ v $ to $ u $ immediately before this operation, there is a directed edge from $ u $ to $ v $ immediately after this operation.
It is guaranteed that, for the given graph, you can reach vertex $ N $ from vertex $ 1 $ by repeating these operations.
Find the minimum total cost required to reach vertex $ N $ .
Input Format
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
> $ N $ $ M $ $ X $ $ u _ 1 $ $ v _ 1 $ $ u _ 2 $ $ v _ 2 $ $ \vdots $ $ u _ M $ $ v _ M $
Output Format
Print the minimum total cost required to reach vertex $ N $ .
Explanation/Hint
### Sample Explanation 1
The given graph looks like this:
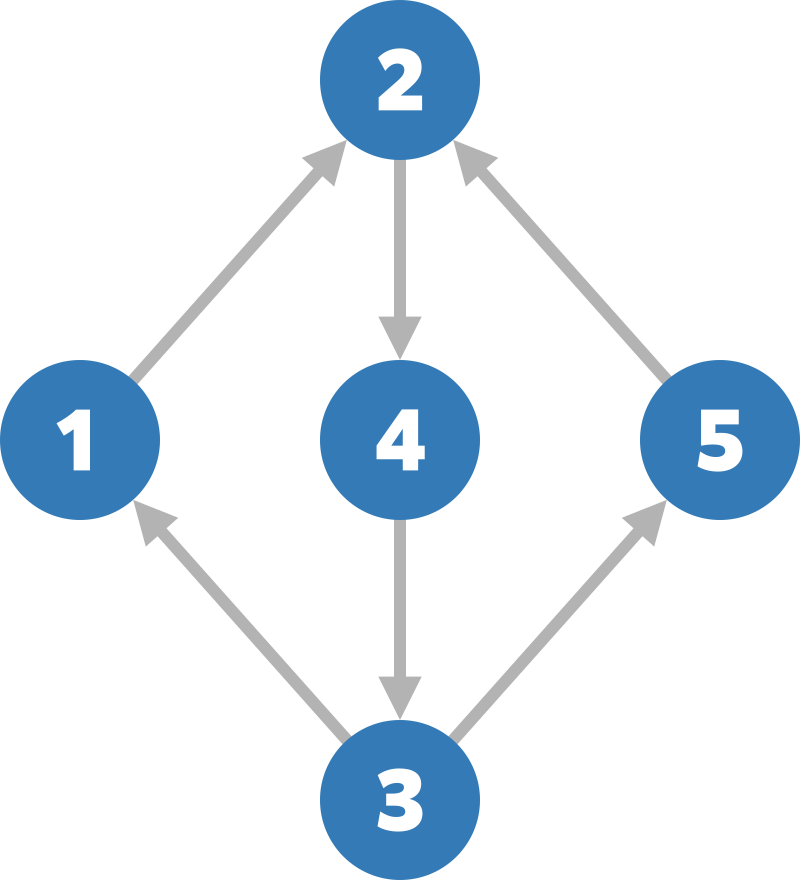
You can reach vertex $ 5 $ with a total cost of $ 4 $ by doing the following:
- Move to vertex $ 2 $ at a cost of $ 1 $ .
- Move to vertex $ 4 $ at a cost of $ 1 $ .
- Move to vertex $ 3 $ at a cost of $ 1 $ .
- Move to vertex $ 5 $ at a cost of $ 1 $ .
It is impossible to reach vertex $ 5 $ with a total cost of $ 3 $ or less, so print `4`.
### Sample Explanation 2
The graph is the same as in Sample 1, but the cost to reverse edges is different.
You can reach vertex 5 with a total cost of $ 3 $ as follows:
- Move to vertex $ 2 $ at a cost of $ 1 $ .
- Reverse all edges at a cost of $ 1 $ .
- Move to vertex $ 5 $ at a cost of $ 1 $ .
It is impossible to reach vertex $ 5 $ with a total cost of $ 2 $ or less, so print `3`.
### Sample Explanation 3
Note that the answer may exceed the $ 32 $ -bit integer range.
### Constraints
- $ 2 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5 $
- $ 1 \leq M \leq 2 \times 10^5 $
- $ 1 \leq X \leq 10^9 $
- $ 1 \leq u _ i \leq N \ (1 \leq i \leq M) $
- $ 1 \leq v _ i \leq N \ (1 \leq i \leq M) $
- For the given graph, it is guaranteed that you can reach vertex $ N $ from vertex $ 1 $ by the operations described.
- All input values are integers.