CF1207C Gas Pipeline
Description
You are responsible for installing a gas pipeline along a road. Let's consider the road (for simplicity) as a segment $ [0, n] $ on $ OX $ axis. The road can have several crossroads, but for simplicity, we'll denote each crossroad as an interval $ (x, x + 1) $ with integer $ x $ . So we can represent the road as a binary string consisting of $ n $ characters, where character 0 means that current interval doesn't contain a crossroad, and 1 means that there is a crossroad.
Usually, we can install the pipeline along the road on height of $ 1 $ unit with supporting pillars in each integer point (so, if we are responsible for $ [0, n] $ road, we must install $ n + 1 $ pillars). But on crossroads we should lift the pipeline up to the height $ 2 $ , so the pipeline won't obstruct the way for cars.
We can do so inserting several zig-zag-like lines. Each zig-zag can be represented as a segment $ [x, x + 1] $ with integer $ x $ consisting of three parts: $ 0.5 $ units of horizontal pipe + $ 1 $ unit of vertical pipe + $ 0.5 $ of horizontal. Note that if pipeline is currently on height $ 2 $ , the pillars that support it should also have length equal to $ 2 $ units.
Each unit of gas pipeline costs us $ a $ bourles, and each unit of pillar — $ b $ bourles. So, it's not always optimal to make the whole pipeline on the height $ 2 $ . Find the shape of the pipeline with minimum possible cost and calculate that cost.
Note that you must start and finish the pipeline on height $ 1 $ and, also, it's guaranteed that the first and last characters of the input string are equal to 0.
Input Format
The fist line contains one integer $ T $ ( $ 1 \le T \le 100 $ ) — the number of queries. Next $ 2 \cdot T $ lines contain independent queries — one query per two lines.
The first line contains three integers $ n $ , $ a $ , $ b $ ( $ 2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ , $ 1 \le a \le 10^8 $ , $ 1 \le b \le 10^8 $ ) — the length of the road, the cost of one unit of the pipeline and the cost of one unit of the pillar, respectively.
The second line contains binary string $ s $ ( $ |s| = n $ , $ s_i \in \{0, 1\} $ , $ s_1 = s_n = 0 $ ) — the description of the road.
It's guaranteed that the total length of all strings $ s $ doesn't exceed $ 2 \cdot 10^5 $ .
Output Format
Print $ T $ integers — one per query. For each query print the minimum possible cost of the constructed pipeline.
Explanation/Hint
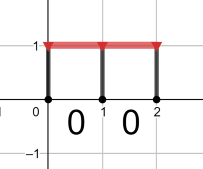
The optimal pipeline for the first query is shown at the picture above.
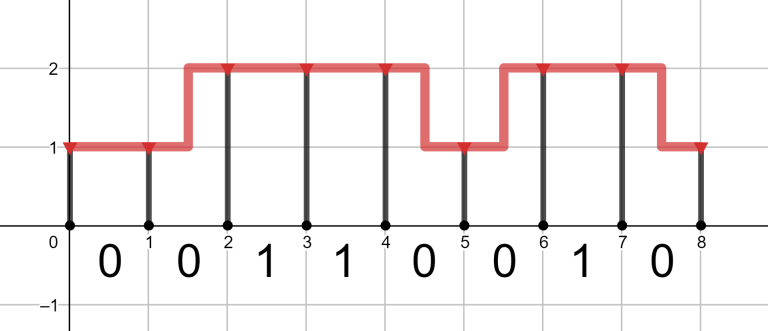
The optimal pipeline for the second query is pictured below:
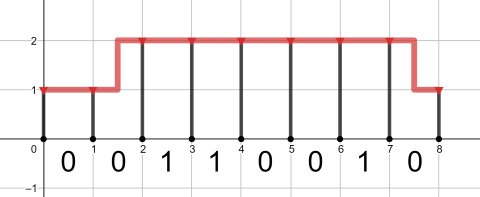The optimal (and the only possible) pipeline for the third query is shown below:
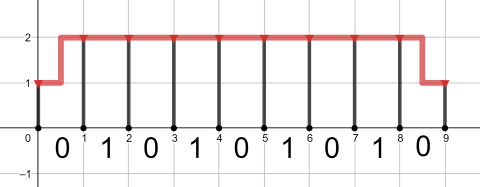The optimal pipeline for the fourth query is shown below: