CF1294E Obtain a Permutation
Description
You are given a rectangular matrix of size $ n \times m $ consisting of integers from $ 1 $ to $ 2 \cdot 10^5 $ .
In one move, you can:
- choose any element of the matrix and change its value to any integer between $ 1 $ and $ n \cdot m $ , inclusive;
- take any column and shift it one cell up cyclically (see the example of such cyclic shift below).
A cyclic shift is an operation such that you choose some $ j $ ( $ 1 \le j \le m $ ) and set $ a_{1, j} := a_{2, j}, a_{2, j} := a_{3, j}, \dots, a_{n, j} := a_{1, j} $ simultaneously.
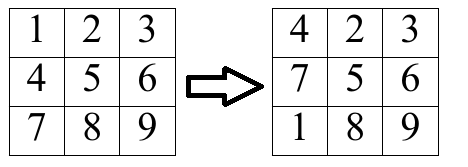 Example of cyclic shift of the first column You want to perform the minimum number of moves to make this matrix look like this:
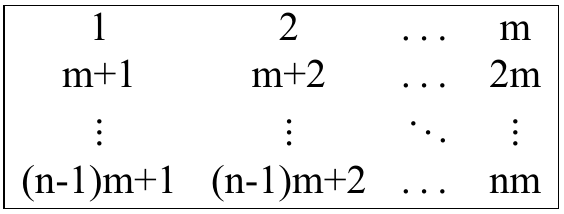In other words, the goal is to obtain the matrix, where $ a_{1, 1} = 1, a_{1, 2} = 2, \dots, a_{1, m} = m, a_{2, 1} = m + 1, a_{2, 2} = m + 2, \dots, a_{n, m} = n \cdot m $ (i.e. $ a_{i, j} = (i - 1) \cdot m + j $ ) with the minimum number of moves performed.
Input Format
The first line of the input contains two integers $ n $ and $ m $ ( $ 1 \le n, m \le 2 \cdot 10^5, n \cdot m \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ ) — the size of the matrix.
The next $ n $ lines contain $ m $ integers each. The number at the line $ i $ and position $ j $ is $ a_{i, j} $ ( $ 1 \le a_{i, j} \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ ).
Output Format
Print one integer — the minimum number of moves required to obtain the matrix, where $ a_{1, 1} = 1, a_{1, 2} = 2, \dots, a_{1, m} = m, a_{2, 1} = m + 1, a_{2, 2} = m + 2, \dots, a_{n, m} = n \cdot m $ ( $ a_{i, j} = (i - 1)m + j $ ).
Explanation/Hint
In the first example, you can set $ a_{1, 1} := 7, a_{1, 2} := 8 $ and $ a_{1, 3} := 9 $ then shift the first, the second and the third columns cyclically, so the answer is $ 6 $ . It can be shown that you cannot achieve a better answer.
In the second example, the matrix is already good so the answer is $ 0 $ .
In the third example, it is enough to shift the second column cyclically twice to obtain a good matrix, so the answer is $ 2 $ .