CF1323B Count Subrectangles
Description
You are given an array $ a $ of length $ n $ and array $ b $ of length $ m $ both consisting of only integers $ 0 $ and $ 1 $ . Consider a matrix $ c $ of size $ n \times m $ formed by following rule: $ c_{i, j} = a_i \cdot b_j $ (i.e. $ a_i $ multiplied by $ b_j $ ). It's easy to see that $ c $ consists of only zeroes and ones too.
How many subrectangles of size (area) $ k $ consisting only of ones are there in $ c $ ?
A subrectangle is an intersection of a consecutive (subsequent) segment of rows and a consecutive (subsequent) segment of columns. I.e. consider four integers $ x_1, x_2, y_1, y_2 $ ( $ 1 \le x_1 \le x_2 \le n $ , $ 1 \le y_1 \le y_2 \le m $ ) a subrectangle $ c[x_1 \dots x_2][y_1 \dots y_2] $ is an intersection of the rows $ x_1, x_1+1, x_1+2, \dots, x_2 $ and the columns $ y_1, y_1+1, y_1+2, \dots, y_2 $ .
The size (area) of a subrectangle is the total number of cells in it.
Input Format
The first line contains three integers $ n $ , $ m $ and $ k $ ( $ 1 \leq n, m \leq 40\,000, 1 \leq k \leq n \cdot m $ ), length of array $ a $ , length of array $ b $ and required size of subrectangles.
The second line contains $ n $ integers $ a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n $ ( $ 0 \leq a_i \leq 1 $ ), elements of $ a $ .
The third line contains $ m $ integers $ b_1, b_2, \ldots, b_m $ ( $ 0 \leq b_i \leq 1 $ ), elements of $ b $ .
Output Format
Output single integer — the number of subrectangles of $ c $ with size (area) $ k $ consisting only of ones.
Explanation/Hint
In first example matrix $ c $ is:
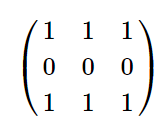There are $ 4 $ subrectangles of size $ 2 $ consisting of only ones in it:
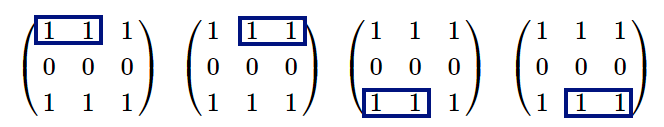In second example matrix $ c $ is: