CF1401A Distance and Axis
Description
We have a point $ A $ with coordinate $ x = n $ on $ OX $ -axis. We'd like to find an integer point $ B $ (also on $ OX $ -axis), such that the absolute difference between the distance from $ O $ to $ B $ and the distance from $ A $ to $ B $ is equal to $ k $ .
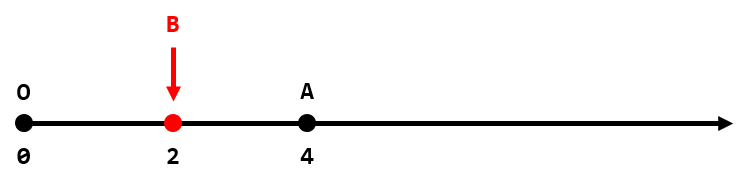The description of the first test case. Since sometimes it's impossible to find such point $ B $ , we can, in one step, increase or decrease the coordinate of $ A $ by $ 1 $ . What is the minimum number of steps we should do to make such point $ B $ exist?
Input Format
The first line contains one integer $ t $ ( $ 1 \le t \le 6000 $ ) — the number of test cases.
The only line of each test case contains two integers $ n $ and $ k $ ( $ 0 \le n, k \le 10^6 $ ) — the initial position of point $ A $ and desirable absolute difference.
Output Format
For each test case, print the minimum number of steps to make point $ B $ exist.
Explanation/Hint
In the first test case (picture above), if we set the coordinate of $ B $ as $ 2 $ then the absolute difference will be equal to $ |(2 - 0) - (4 - 2)| = 0 $ and we don't have to move $ A $ . So the answer is $ 0 $ .
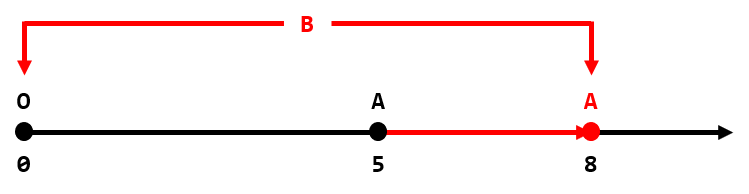
In the second test case, we can increase the coordinate of $ A $ by $ 3 $ and set the coordinate of $ B $ as $ 0 $ or $ 8 $ . The absolute difference will be equal to $ |8 - 0| = 8 $ , so the answer is $ 3 $ .