CF1491H Yuezheng Ling and Dynamic Tree
Description
Yuezheng Ling gives Luo Tianyi a tree which has $ n $ nodes, rooted at $ 1 $ .
Luo Tianyi will tell you that the parent of the $ i $ -th node is $ a_i $ ( $ 1 \leq a_i
Input Format
The first line contains two integers $ n $ and $ q $ ( $ 2\leq n,q \leq 10^5 $ ) — the number of nodes and the number of queries, respectively.
The second line contains $ n-1 $ integers $ a_2, a_3,\dots, a_n $ ( $ 1 \le a_i < i $ ), where $ a_i $ is the parent of the node $ i $ .
Next $ q $ lines contain queries. For each query, the first integer of each line is $ t $ ( $ t = 1 $ or $ 2 $ ) — the type of the query.
If $ t = 1 $ , this represents the query of the first type. Then, three integers will follow: $ l $ , $ r $ , $ x $ ( $ 2 \le l \le r \le n $ , $ 1 \le x \le 10^5 $ ), meaning that you have to replace $ a_i $ with $ \max(a_i-x,1) $ for all $ i $ with $ l \leq i \leq r $ .
If $ t = 2 $ , this represents the query of the second type. Then, two integers will follow: $ u $ and $ v $ ( $ 1 \le u, v \le n $ ), and you have to find the LCA of $ u $ and $ v $ .
It's guaranteed that there is at least one query of the second type.
Output Format
For each query of the second type output answer on a new line.
Explanation/Hint
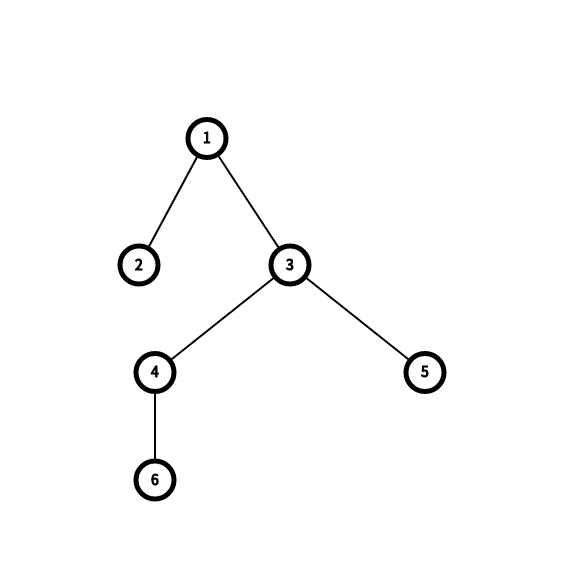
The tree in example is shown below.
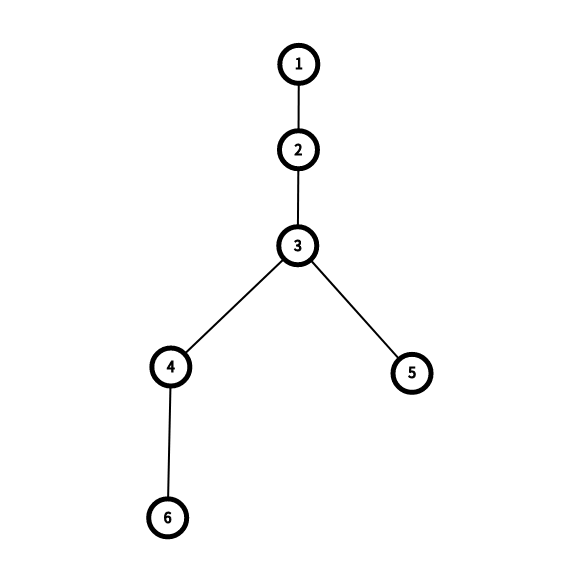After the query of the first type, the tree changes and is looking as shown below.