CF1540B Tree Array
题目描述
给定一棵包含 $n$ 个节点的树。你需要通过逐个标记节点的方式,从树中生成一个数组。
最开始,没有任何节点被标记,从整棵树中等概率地选择一个节点并将其标记。
之后,直到所有节点都被标记为止,每次从所有与已标记节点有至少一条边相连的未标记节点中,等概率地选择一个节点并将其标记。
可以证明,这一过程最终会标记树中的所有节点。
最终得到的数组 $a$,是按照每个节点被标记的时间顺序排列的节点编号。
请你求出通过上述过程生成的数组中,期望的逆序对数量。
数组 $a$ 中的逆序对数量,定义为满足 $i < j$ 且 $a_i > a_j$ 的下标对 $(i, j)$ 的个数。例如,数组 $[4, 1, 3, 2]$ 包含 $4$ 个逆序对:$(1, 2)$、$(1, 3)$、$(1, 4)$、$(3, 4)$。
输入格式
第一行包含一个整数 $n$($2 \le n \le 200$),表示树的节点数。
接下来的 $n-1$ 行,每行包含两个整数 $x$ 和 $y$($1 \le x, y \le n$,$x \neq y$),表示节点 $x$ 和节点 $y$ 之间有一条边。
保证给定的边构成一棵树。
输出格式
输出通过上述过程生成的数组中,期望的逆序对数量,结果对 $10^9+7$ 取模。
形式化地,设 $M = 10^9+7$。可以证明,答案可以表示为最简分数 $\frac{p}{q}$,其中 $p$ 和 $q$ 是整数,且 $q \not\equiv 0 \pmod{M}$。请输出一个整数 $x$,满足 $0 \le x < M$ 且 $x \cdot q \equiv p \pmod{M}$。换句话说,输出满足条件的 $x$。
说明/提示
下面是第一个样例的树结构:
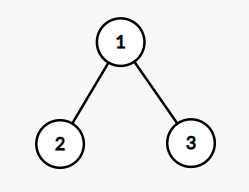
对于第一个样例,数组几乎是固定的。如果最初选择节点 $2$,唯一可能的数组是 $[2, 1, 3]$($1$ 个逆序对)。如果最初选择节点 $3$,唯一可能的数组是 $[3, 1, 2]$($2$ 个逆序对)。如果最初选择节点 $1$,唯一可能的数组是 $[1, 2, 3]$($0$ 个逆序对)和 $[1, 3, 2]$($1$ 个逆序对),且这两种情况等概率。总的期望逆序对数量为 $\frac{1}{3}\cdot 1 + \frac{1}{3} \cdot 2 + \frac{1}{3} \cdot (\frac{1}{2} \cdot 0 + \frac{1}{2} \cdot 1) = \frac{7}{6}$。
$166666669 \cdot 6 = 7 \pmod {10^9 + 7}$,所以答案是 $166666669$。
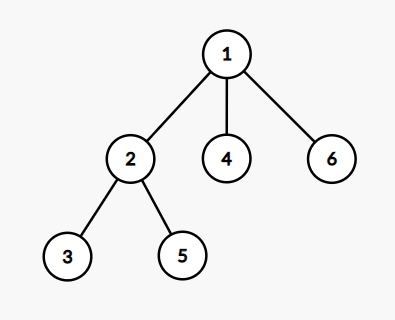
下面是第二个样例的树结构:
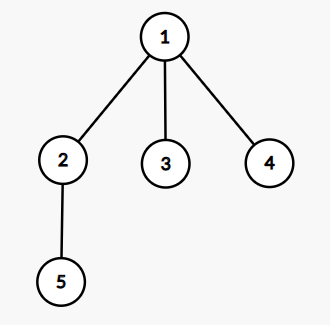
下面是第三个样例的树结构:
由 ChatGPT 4.1 翻译