CF1575M Managing Telephone Poles
Description
Mr. Chanek's city can be represented as a plane. He wants to build a housing complex in the city.
There are some telephone poles on the plane, which is represented by a grid $ a $ of size $ (n + 1) \times (m + 1) $ . There is a telephone pole at $ (x, y) $ if $ a_{x, y} = 1 $ .
For each point $ (x, y) $ , define $ S(x, y) $ as the square of the Euclidean distance between the nearest pole and $ (x, y) $ . Formally, the square of the Euclidean distance between two points $ (x_1, y_1) $ and $ (x_2, y_2) $ is $ (x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2 $ .
To optimize the building plan, the project supervisor asks you the sum of all $ S(x, y) $ for each $ 0 \leq x \leq n $ and $ 0 \leq y \leq m $ . Help him by finding the value of $ \sum_{x=0}^{n} {\sum_{y=0}^{m} {S(x, y)}} $ .
Input Format
The first line contains two integers $ n $ and $ m $ ( $ 0 \leq n, m < 2000 $ ) — the size of the grid.
Then $ (n + 1) $ lines follow, each containing $ (m + 1) $ integers $ a_{i, j} $ ( $ 0 \leq a_{i, j} \leq 1 $ ) — the grid denoting the positions of telephone poles in the plane. There is at least one telephone pole in the given grid.
Output Format
Output an integer denoting the value of $ \sum_{x=0}^{n} {\sum_{y=0}^{m} {S(x, y)}} $ .
Explanation/Hint
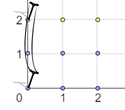In the first example, the nearest telephone pole for the points $ (0,0) $ , $ (1,0) $ , $ (2,0) $ , $ (0,1) $ , $ (1,1) $ , and $ (2,1) $ is at $ (0, 0) $ . While the nearest telephone pole for the points $ (0, 2) $ , $ (1,2) $ , and $ (2,2) $ is at $ (0, 2) $ . Thus, $ \sum_{x=0}^{n} {\sum_{y=0}^{m} {S(x, y)}} = (0 + 1 + 4) + (1 + 2 + 5) + (0 + 1 + 4) = 18 $ .