CF1633E Spanning Tree Queries
Description
You are given a connected weighted undirected graph, consisting of $ n $ vertices and $ m $ edges.
You are asked $ k $ queries about it. Each query consists of a single integer $ x $ . For each query, you select a spanning tree in the graph. Let the weights of its edges be $ w_1, w_2, \dots, w_{n-1} $ . The cost of a spanning tree is $ \sum \limits_{i=1}^{n-1} |w_i - x| $ (the sum of absolute differences between the weights and $ x $ ). The answer to a query is the lowest cost of a spanning tree.
The queries are given in a compressed format. The first $ p $ $ (1 \le p \le k) $ queries $ q_1, q_2, \dots, q_p $ are provided explicitly. For queries from $ p+1 $ to $ k $ , $ q_j = (q_{j-1} \cdot a + b) \mod c $ .
Print the xor of answers to all queries.
Input Format
The first line contains two integers $ n $ and $ m $ ( $ 2 \le n \le 50 $ ; $ n - 1 \le m \le 300 $ ) — the number of vertices and the number of edges in the graph.
Each of the next $ m $ lines contains a description of an undirected edge: three integers $ v $ , $ u $ and $ w $ ( $ 1 \le v, u \le n $ ; $ v \neq u $ ; $ 0 \le w \le 10^8 $ ) — the vertices the edge connects and its weight. Note that there might be multiple edges between a pair of vertices. The edges form a connected graph.
The next line contains five integers $ p, k, a, b $ and $ c $ ( $ 1 \le p \le 10^5 $ ; $ p \le k \le 10^7 $ ; $ 0 \le a, b \le 10^8 $ ; $ 1 \le c \le 10^8 $ ) — the number of queries provided explicitly, the total number of queries and parameters to generate the queries.
The next line contains $ p $ integers $ q_1, q_2, \dots, q_p $ ( $ 0 \le q_j < c $ ) — the first $ p $ queries.
Output Format
Print a single integer — the xor of answers to all queries.
Explanation/Hint
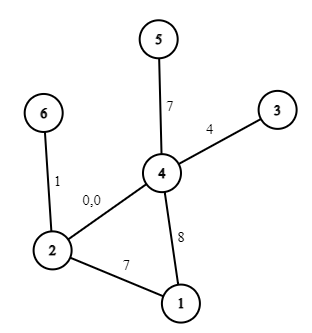
The queries in the first example are $ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 $ . The answers are $ 11, 9, 7, 3, 1, 5, 8, 7, 5, 7, 11 $ .
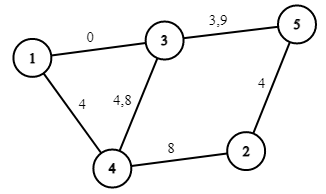The queries in the second example are $ 3, 0, 2, 1, 6, 0, 3, 5, 4, 1 $ . The answers are $ 14, 19, 15, 16, 11, 19, 14, 12, 13, 16 $ .
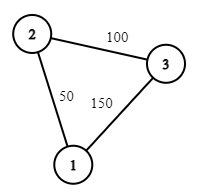
The queries in the third example are $ 75, 0, 0, \dots $ . The answers are $ 50, 150, 150, \dots $ .