CF1650G Counting Shortcuts
Description
Given an undirected connected graph with $ n $ vertices and $ m $ edges. The graph contains no loops (edges from a vertex to itself) and multiple edges (i.e. no more than one edge between each pair of vertices). The vertices of the graph are numbered from $ 1 $ to $ n $ .
Find the number of paths from a vertex $ s $ to $ t $ whose length differs from the shortest path from $ s $ to $ t $ by no more than $ 1 $ . It is necessary to consider all suitable paths, even if they pass through the same vertex or edge more than once (i.e. they are not simple).
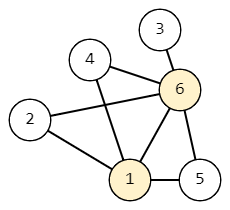Graph consisting of $ 6 $ of vertices and $ 8 $ of edgesFor example, let $ n = 6 $ , $ m = 8 $ , $ s = 6 $ and $ t = 1 $ , and let the graph look like the figure above. Then the length of the shortest path from $ s $ to $ t $ is $ 1 $ . Consider all paths whose length is at most $ 1 + 1 = 2 $ .
- $ 6 \rightarrow 1 $ . The length of the path is $ 1 $ .
- $ 6 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 1 $ . Path length is $ 2 $ .
- $ 6 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 1 $ . Path length is $ 2 $ .
- $ 6 \rightarrow 5 \rightarrow 1 $ . Path length is $ 2 $ .
There is a total of $ 4 $ of matching paths.
Input Format
The first line of test contains the number $ t $ ( $ 1 \le t \le 10^4 $ ) —the number of test cases in the test.
Before each test case, there is a blank line.
The first line of test case contains two numbers $ n, m $ ( $ 2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ , $ 1 \le m \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ ) —the number of vertices and edges in the graph.
The second line contains two numbers $ s $ and $ t $ ( $ 1 \le s, t \le n $ , $ s \neq t $ ) —the numbers of the start and end vertices of the path.
The following $ m $ lines contain descriptions of edges: the $ i $ th line contains two integers $ u_i $ , $ v_i $ ( $ 1 \le u_i,v_i \le n $ ) — the numbers of vertices that connect the $ i $ th edge. It is guaranteed that the graph is connected and does not contain loops and multiple edges.
It is guaranteed that the sum of values $ n $ on all test cases of input data does not exceed $ 2 \cdot 10^5 $ . Similarly, it is guaranteed that the sum of values $ m $ on all test cases of input data does not exceed $ 2 \cdot 10^5 $ .
Output Format
For each test case, output a single number — the number of paths from $ s $ to $ t $ such that their length differs from the length of the shortest path by no more than $ 1 $ .
Since this number may be too large, output it modulo $ 10^9 + 7 $ .