CF1764H Doremy's Paint 2
Description
Doremy has $ n $ buckets of paint which is represented by an array $ a $ of length $ n $ . Bucket $ i $ contains paint with color $ a_i $ . Initially, $ a_i=i $ .
Doremy has $ m $ segments $ [l_i,r_i] $ ( $ 1 \le l_i \le r_i \le n $ ). Each segment describes an operation. Operation $ i $ is performed as follows:
- For each $ j $ such that $ l_i < j \leq r_i $ , set $ a_j := a_{l_i} $ .
Doremy also selects an integer $ k $ . She wants to know for each integer $ x $ from $ 0 $ to $ m-1 $ , the number of distinct colors in the array after performing operations $ x \bmod m +1, (x+1) \bmod m + 1, \ldots, (x+k-1) \bmod m +1 $ . Can you help her calculate these values? Note that for each $ x $ individually we start from the initial array and perform only the given $ k $ operations in the given order.
Input Format
The first line of input contains three integers $ n $ , $ m $ , and $ k $ ( $ 1\le n,m\le 2\cdot 10^5 $ , $ 1 \le k \le m $ ) — the length of the array $ a $ , the total number of operations, and the integer that Doremy selects.
The $ i $ -th line of the following $ m $ lines contains two integers $ l_i $ , $ r_i $ ( $ 1\le l_i\le r_i\le n $ ) — the bounds of the $ i $ -th segment.
Output Format
Output $ m $ integers. The $ (x+1) $ -th integer should be the number of distinct colors in the array if we start from the initial array and perform operations $ x \bmod m +1, (x+1) \bmod m + 1, \ldots, (x+k-1) \bmod m +1 $ .
Explanation/Hint
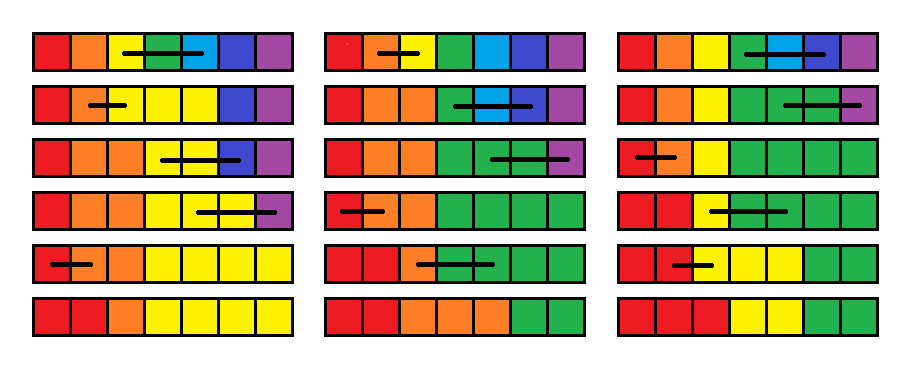
In the first test case, the picture below shows the resulting array for the values of $ x=0,1,2 $ respectively.