CF1778F Maximizing Root
Description
You are given a rooted tree consisting of $ n $ vertices numbered from $ 1 $ to $ n $ . Vertex $ 1 $ is the root of the tree. Each vertex has an integer value. The value of $ i $ -th vertex is $ a_i $ . You can do the following operation at most $ k $ times.
- Choose a vertex $ v $ that has not been chosen before and an integer $ x $ such that $ x $ is a common divisor of the values of all vertices of the subtree of $ v $ . Multiply by $ x $ the value of each vertex in the subtree of $ v $ .
What is the maximum possible value of the root node $ 1 $ after at most $ k $ operations? Formally, you have to maximize the value of $ a_1 $ .
A tree is a connected undirected graph without cycles. A rooted tree is a tree with a selected vertex, which is called the root. The subtree of a node $ u $ is the set of all nodes $ y $ such that the simple path from $ y $ to the root passes through $ u $ . Note that $ u $ is in the subtree of $ u $ .
Input Format
The first line contains an integer $ t $ ( $ 1 \leq t \leq 50\,000 $ ) — the number of test cases. The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two integers $ n $ and $ k $ ( $ 2 \leq n \leq 10^5 $ , $ 0 \leq k \leq n $ ) — the number of vertices in the tree and the number of operations.
The second line contains $ n $ integers $ a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n $ ( $ 1 \leq a_i \leq 1000 $ ), where $ a_i $ denotes the value of vertex $ i $ .
Each of the next $ n - 1 $ lines contains two integers $ u_i $ and $ v_i $ ( $ 1 \leq u_i, v_i \leq n $ , $ u_i \neq v_i $ ), denoting the edge of the tree between vertices $ u_i $ and $ v_i $ . It is guaranteed that the given edges form a tree.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $ n $ over all test cases does not exceed $ 2 \cdot 10^5 $ .
Output Format
For each test case, output the maximum value of the root after performing at most $ k $ operations.
Explanation/Hint
Both examples have the same tree:
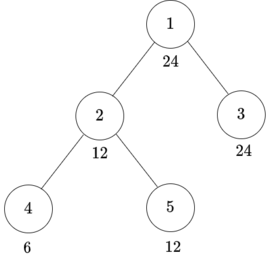For the first test case, you can do two operations as follows:
- Choose the subtree of vertex $ 4 $ and $ x = 2 $ . 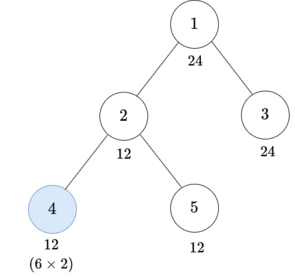 After this operation, the node values become $ \{24, 12, 24, 12, 12\}. $
- Choose the subtree of vertex $ 1 $ and $ x = 12 $ . 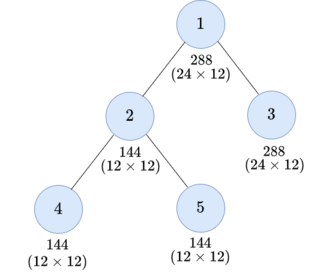 After this operation, the node values become $ \{288, 144, 288, 144, 144\}. $
The value of the root is $ 288 $ and it is the maximum.For the second test case, you can do three operations as follows:
- Choose the subtree of vertex $ 4 $ and $ x = 2 $ .  After this operation, the node values become $ \{24, 12, 24, 12, 12\}. $
- Choose the subtree of vertex $ 2 $ and $ x = 4 $ . 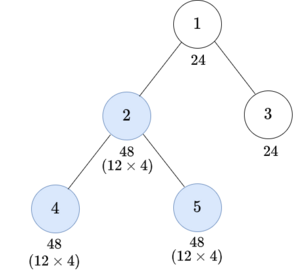 After this operation, the node values become $ \{24, 48, 24, 48, 48\}. $
- Choose the subtree of vertex $ 1 $ and $ x = 24 $ . 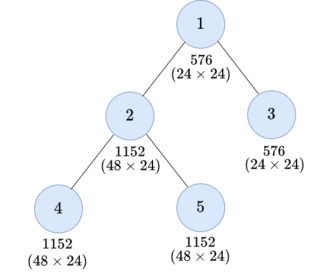 After this operation, the node values become $ \{576, 1152, 576, 1152, 1152\}. $
The value of the root is $ 576 $ and it is the maximum.