CF1797D Li Hua and Tree
Description
Li Hua has a tree of $ n $ vertices and $ n-1 $ edges. The root of the tree is vertex $ 1 $ . Each vertex $ i $ has importance $ a_i $ . Denote the size of a subtree as the number of vertices in it, and the importance as the sum of the importance of vertices in it. Denote the heavy son of a non-leaf vertex as the son with the largest subtree size. If multiple of them exist, the heavy son is the one with the minimum index.
Li Hua wants to perform $ m $ operations:
- "1 $ x $ " ( $ 1\leq x \leq n $ ) — calculate the importance of the subtree whose root is $ x $ .
- "2 $ x $ " ( $ 2\leq x \leq n $ ) — rotate the heavy son of $ x $ up. Formally, denote $ son_x $ as the heavy son of $ x $ , $ fa_x $ as the father of $ x $ . He wants to remove the edge between $ x $ and $ fa_x $ and connect an edge between $ son_x $ and $ fa_x $ . It is guaranteed that $ x $ is not root, but not guaranteed that $ x $ is not a leaf. If $ x $ is a leaf, please ignore the operation.
Suppose you were Li Hua, please solve this problem.
Input Format
The first line contains 2 integers $ n,m $ ( $ 2\le n\le 10^{5},1\le m\le 10^{5} $ ) — the number of vertices in the tree and the number of operations.
The second line contains $ n $ integers $ a_{1},a_{2},\ldots ,a_{n} $ ( $ -10^{9}\le a_{i}\le 10^{9} $ ) — the importance of each vertex.
Next $ n-1 $ lines contain the edges of the tree. The $ i $ -th line contains two integers $ u_i $ and $ v_i $ ( $ 1\le u_i,v_i\le n $ , $ u_i\ne v_i $ ) — the corresponding edge. The given edges form a tree.
Next $ m $ lines contain operations — one operation per line. The $ j $ -th operation contains two integers $ t_{j},x_{j} $ ( $ t_{j}\in \{1,2\} $ , $ 1 \leq x_{j} \leq n $ , $ x_{j}\neq 1 $ if $ t_j = 2 $ ) — the $ j $ -th operation.
Output Format
For each query "1 $ x $ ", output the answer in an independent line.
Explanation/Hint
In the first example:
The initial tree is shown in the following picture:
The importance of the subtree of $ 6 $ is $ a_6+a_7=2 $ .
After rotating the heavy son of $ 3 $ (which is $ 6 $ ) up, the tree is shown in the following picture:
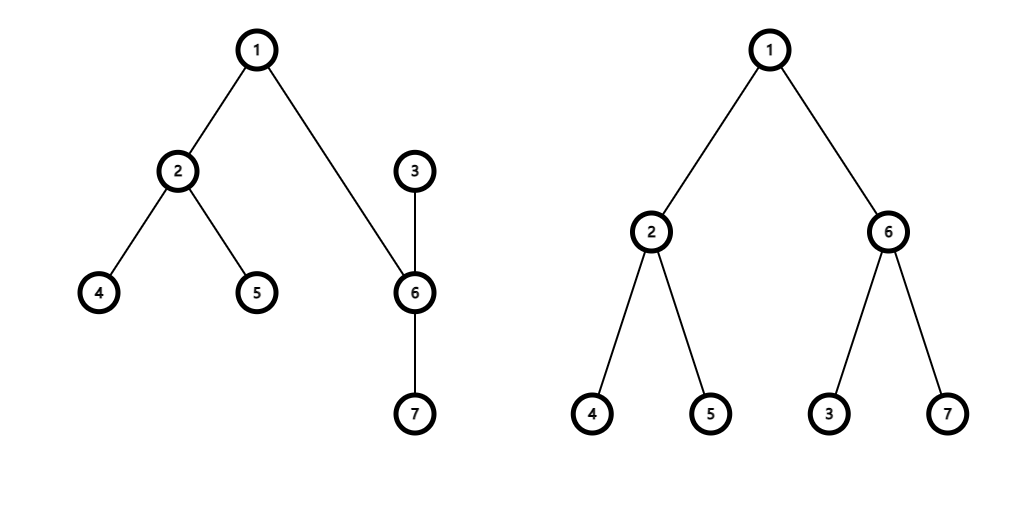The importance of the subtree of $ 6 $ is $ a_6+a_3+a_7=3 $ .
The importance of the subtree of $ 2 $ is $ a_2+a_4+a_5=3 $ .