CF1842E Tenzing and Triangle
Description
There are $ n $ pairwise-distinct points and a line $ x+y=k $ on a two-dimensional plane. The $ i $ -th point is at $ (x_i,y_i) $ . All points have non-negative coordinates and are strictly below the line. Alternatively, $ 0 \leq x_i,y_i, x_i+y_i < k $ .
Tenzing wants to erase all the points. He can perform the following two operations:
1. Draw triangle: Tenzing will choose two non-negative integers $ a $ , $ b $ that satisfy $ a+b
Input Format
The first line of the input contains three integers $ n $ , $ k $ and $ A $ ( $ 1\leq n,k\leq 2\cdot 10^5 $ , $ 1\leq A\leq 10^4 $ ) — the number of points, the coefficient describing the hypotenuse of the triangle and the coefficient describing the cost of drawing a triangle.
The following $ n $ lines of the input the $ i $ -th line contains three integers $ x_i,y_i,c_i $ ( $ 0\leq x_i,y_i,x_i+y_i< k $ , $ 1\leq c_i\leq 10^4 $ ) — the coordinate of the $ i $ -th points and the cost of erasing it using the second operation. It is guaranteed that the coordinates are pairwise distinct.
Output Format
Output a single integer —the minimum cost needed to erase all of the points.
Explanation/Hint
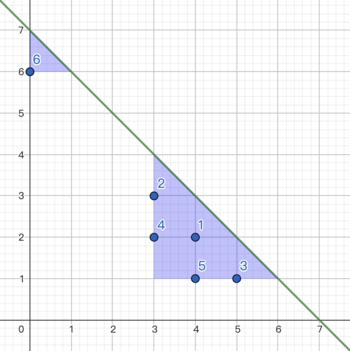
The picture of the first example:
Tenzing do the following operations:
1. draw a triangle with $ a=3,b=2 $ , the cost $ =1\cdot A=1 $ .
2. erase the first point, the cost $ =1 $ .
3. erase the second point, the cost $ =1 $ .
4. erase the third point, the cost $ =1 $ .
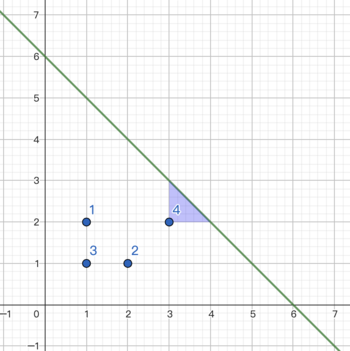The picture of the second example: