CF1937B Binary Path
Description
You are given a $ 2 \times n $ grid filled with zeros and ones. Let the number at the intersection of the $ i $ -th row and the $ j $ -th column be $ a_{ij} $ .
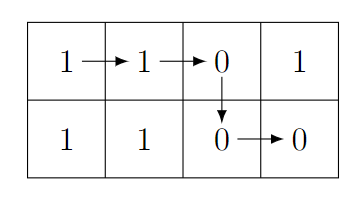
There is a grasshopper at the top-left cell $ (1, 1) $ that can only jump one cell right or downwards. It wants to reach the bottom-right cell $ (2, n) $ . Consider the binary string of length $ n+1 $ consisting of numbers written in cells of the path without changing their order.
Your goal is to:
1. Find the lexicographically smallest $ ^\dagger $ string you can attain by choosing any available path;
2. Find the number of paths that yield this lexicographically smallest string.
$ ^\dagger $ If two strings $ s $ and $ t $ have the same length, then $ s $ is lexicographically smaller than $ t $ if and only if in the first position where $ s $ and $ t $ differ, the string $ s $ has a smaller element than the corresponding element in $ t $ .
Input Format
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases $ t $ ( $ 1 \le t \le 10^4 $ ). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer $ n $ ( $ 2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ ).
The second line of each test case contains a binary string $ a_{11} a_{12} \ldots a_{1n} $ ( $ a_{1i} $ is either $ 0 $ or $ 1 $ ).
The third line of each test case contains a binary string $ a_{21} a_{22} \ldots a_{2n} $ ( $ a_{2i} $ is either $ 0 $ or $ 1 $ ).
It is guaranteed that the sum of $ n $ over all test cases does not exceed $ 2 \cdot 10^5 $ .
Output Format
For each test case, output two lines:
1. The lexicographically smallest string you can attain by choosing any available path;
2. The number of paths that yield this string.
Explanation/Hint
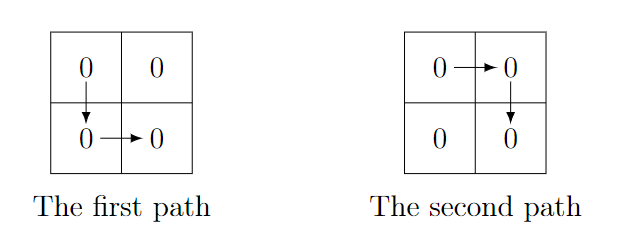
In the first test case, the lexicographically smallest string is $ \mathtt{000} $ . There are two paths that yield this string:
In the second test case, the lexicographically smallest string is $ \mathtt{11000} $ . There is only one path that yields this string: