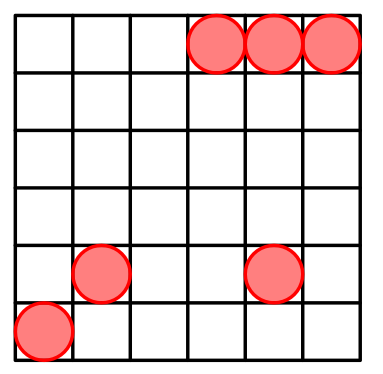
CF1968E Cells Arrangement
Description
You are given an integer $ n $ . You choose $ n $ cells $ (x_1,y_1), (x_2,y_2),\dots,(x_n,y_n) $ in the grid $ n\times n $ where $ 1\le x_i\le n $ and $ 1\le y_i\le n $ .
Let $ \mathcal{H} $ be the set of distinct Manhattan distances between any pair of cells. Your task is to maximize the size of $ \mathcal{H} $ . Examples of sets and their construction are given in the notes.
If there exists more than one solution, you are allowed to output any.
Manhattan distance between cells $ (x_1,y_1) $ and $ (x_2,y_2) $ equals $ |x_1-x_2|+|y_1-y_2| $ .
Input Format
The first line contains a single integer $ t $ ( $ 1\le t\le 50 $ ) — the number of test cases.
Each of the following $ t $ lines contains a single integer $ n $ ( $ 2\le n\le 10^3 $ ).
Output Format
For each test case, output $ n $ points which maximize the size of $ \mathcal{H} $ . It is not necessary to output an empty line at the end of the answer for each test case.
Explanation/Hint
In the first testcase we have $ n=2 $ . One of the possible arrangements is:
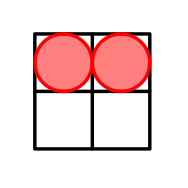 The arrangement with cells located in $ (1,1) $ and $ (1,2) $ . In this case $ \mathcal{H}=\{|1-1|+|1-1|,|1-1|+|2-2|,|1-1|+|1-2|\}=\{0,0,1\}=\{0,1\} $ . Hence, the size of $ \mathcal{H} $ is $ 2 $ . It can be shown that it is the greatest possible answer.In the second testcase we have $ n=3 $ . The optimal arrangement is:
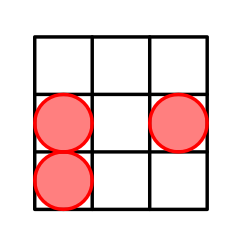 The arrangement with cells located in $ (2,1) $ , $ (2,3) $ and $ (3,1) $ . $ \mathcal{H} $ = $ \{|2-2|+|1-1|,|2-2|+|3-3|,|3-3|+|1-1|,|2-2|+|1-3|,|2-3|+|1-1|,|2-3|+|3-1|\} $ = $ \{0,0,0,2,1,3\} $ = $ \{0,1,2,3\} $ .
For $ n=4 $ a possible arrangement is:
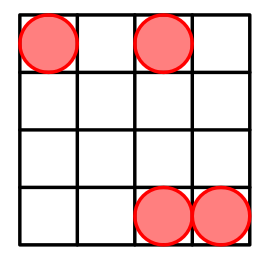For $ n=5 $ a possible arrangement is:
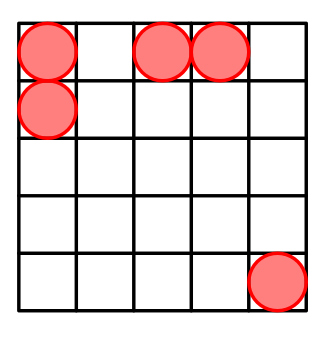For $ n=6 $ a possible arrangement is: