CF1971D Binary Cut
题目描述
给定一个二进制字符串 $ ^{\dagger} $ 。请找到您需要将其切割成的最小片段数,将生成的片段重新排列成有序的二进制字符串。
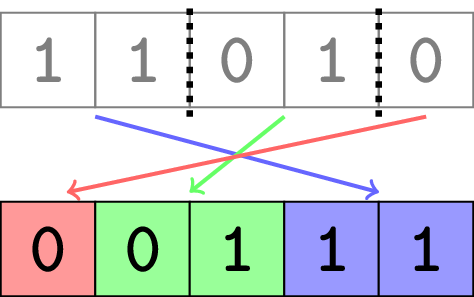
请注意:
- 每个字符必须恰好位于其中一个片段中;
- 这些片段必须是原始字符串的连续子字符串;
- 你必须在重排中使用所有的片段。
$^{\dagger}$二进制字符串是由字符 $ \texttt{0}$ 和 $\texttt{1}$ 组成的字符串。排序后的二进制字符串是一个二进制字符串,使得所有字符 $\texttt{0}$ 位于所有字符 $\texttt{1}$ 之前。
输入格式
第一行包含一个整数 $t$($1\leq t\leq 500$)——测试用例的数量。
每个测试用例的唯一一行包含一个由 $\texttt{0}$ 和 $\texttt1$ 组成的字符串 $s$ ($1 \leq |s| \leq 500$),其中 $|s|$ 表示字符串 $s$ 的长度。
输出格式
对于每个测试用例,输出将字符串重新排列为有序二进制字符串所需的最小分割数量。
说明/提示
The first test case is pictured in the statement. It can be proven that you can't use fewer than $ 3 $ pieces.
In the second and third test cases, the binary string is already sorted, so only $ 1 $ piece is needed.
In the fourth test case, you need to make a single cut between the two characters and rearrange them to make the string $ \texttt{01} $ .