CF2194D Table Cut
Description
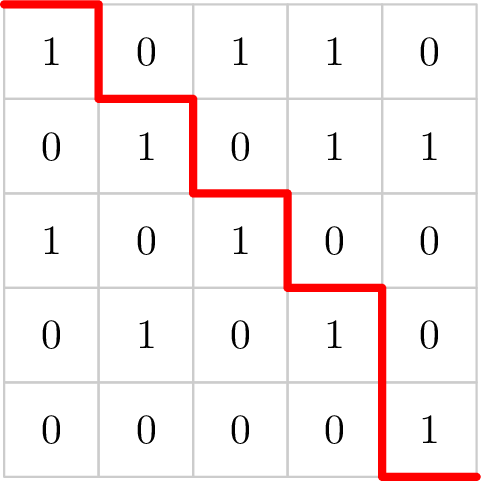
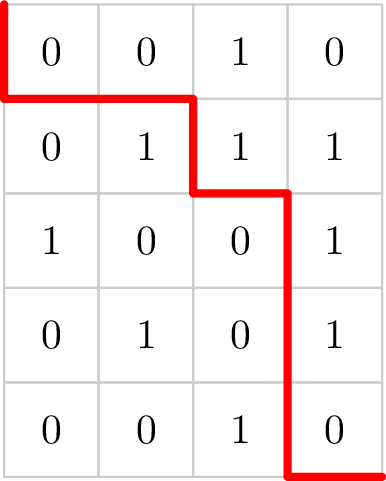
Given a table of size $ n \times m $ , where each cell contains either $ 0 $ or $ 1 $ . The task is to divide it into two parts with a cut that goes from the top left corner to the bottom right corner. The cut lines can only go right or down.
Let $ a $ be the number of ones in one part of the table after the cut, and $ b $ be the number of ones in the other part of the table. The goal is to maximize the value of $ a \cdot b $ .
Input Format
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases $ t $ ( $ 1 \le t \le 10^4 $ ). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two integers $ n $ and $ m $ ( $ 1 \leq n, m \leq 3 \cdot 10^{5} $ , $ 2 \leq n \cdot m \leq 3 \cdot 10^{5} $ ) — the number of rows and columns in the table, respectively.
Each of the following $ n $ lines contains $ m $ integers, where the $ j $ -th number in the $ i $ -th line corresponds to the value $ a_{i, j} $ ( $ 0 \leq a_{i, j} \leq 1 $ ).
It is guaranteed that the sum of $ n \cdot m $ across all test cases does not exceed $ 3 \cdot 10^{5} $ .
Output Format
For each test case, output a single number in the first line of the output data — the maximum value of the product.
In the second line, output a string consisting of $ n $ characters 'D' and $ m $ characters 'R', representing the direction of the next cut, where 'D' means a cut downwards, and 'R' — a cut to the right.
Explanation/Hint
The images show the correct cuts for each of the first and second test cases, at which the maximum value of the product is achieved.