CF228B Two Tables
Description
You've got two rectangular tables with sizes $ n_{a}×m_{a} $ and $ n_{b}×m_{b} $ cells. The tables consist of zeroes and ones. We will consider the rows and columns of both tables indexed starting from 1. Then we will define the element of the first table, located at the intersection of the $ i $ -th row and the $ j $ -th column, as $ a_{i,j} $ ; we will define the element of the second table, located at the intersection of the $ i $ -th row and the $ j $ -th column, as $ b_{i,j} $ .
We will call the pair of integers $ (x,y) $ a shift of the second table relative to the first one. We'll call the overlap factor of the shift $ (x,y) $ value:
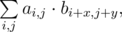where the variables $ i,j $ take only such values, in which the expression $ a_{i,j}·b_{i+x,j+y} $ makes sense. More formally, inequalities $ 1
Input Format
The first line contains two space-separated integers $ n_{a},m_{a} $ $ (1
Output Format
Print two space-separated integers $ x,y $ $ (|x|,|y|