CF228D Zigzag
Description
The court wizard Zigzag wants to become a famous mathematician. For that, he needs his own theorem, like the Cauchy theorem, or his sum, like the Minkowski sum. But most of all he wants to have his sequence, like the Fibonacci sequence, and his function, like the Euler's totient function.
The Zigag's sequence with the zigzag factor z is an infinite sequence $ S_{i}^{z} $ $ (i>=1; z>=2) $ , that is determined as follows:
- $ S_{i}^{z}=2 $ , when 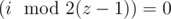;
- 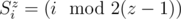, when 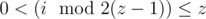;
- 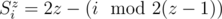, when 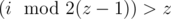.
Operation 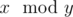 means taking the remainder from dividing number $ x $ by number $ y $ . For example, the beginning of sequence $ S_{i}^{3} $ (zigzag factor 3) looks as follows: 1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 1.
Let's assume that we are given an array $ a $ , consisting of $ n $ integers. Let's define element number $ i $ $ (1
Input Format
The first line contains integer $ n $ $ (1
Output Format
For each Zigzag operation print the calculated value of the Zigzag function on a single line. Print the values for Zigzag functions in the order, in which they are given in the input.
Please, do not use the %lld specifier to read or write 64-bit integers in С++. It is preferred to use cin, cout streams or the %I64d specifier.
Explanation/Hint
Explanation of the sample test:
- Result of the first operation is $ Z(2,3,2)=3·1+1·2=5 $ .
- Result of the second operation is $ Z(1,5,3)=2·1+3·2+1·3+5·2+5·1=26 $ .
- After the third operation array $ a $ is equal to $ 2,3,5,5,5 $ .
- Result of the forth operation is $ Z(1,5,3)=2·1+3·2+5·3+5·2+5·1=38 $ .