CF472C Design Tutorial: Make It Nondeterministic
Description
A way to make a new task is to make it nondeterministic or probabilistic. For example, the hard task of Topcoder SRM 595, Constellation, is the probabilistic version of a convex hull.
Let's try to make a new task. Firstly we will use the following task. There are $ n $ people, sort them by their name. It is just an ordinary sorting problem, but we can make it more interesting by adding nondeterministic element. There are $ n $ people, each person will use either his/her first name or last name as a handle. Can the lexicographical order of the handles be exactly equal to the given permutation $ p $ ?
More formally, if we denote the handle of the $ i $ -th person as $ h_{i} $ , then the following condition must hold: 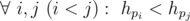.
Input Format
A way to make a new task is to make it nondeterministic or probabilistic. For example, the hard task of Topcoder SRM 595, Constellation, is the probabilistic version of a convex hull.
Let's try to make a new task. Firstly we will use the following task. There are $ n $ people, sort them by their name. It is just an ordinary sorting problem, but we can make it more interesting by adding nondeterministic element. There are $ n $ people, each person will use either his/her first name or last name as a handle. Can the lexicographical order of the handles be exactly equal to the given permutation $ p $ ?
More formally, if we denote the handle of the $ i $ -th person as $ h_{i} $ , then the following condition must hold: 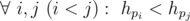.
Output Format
If it is possible, output "YES", otherwise output "NO".
Explanation/Hint
In example 1 and 2, we have 3 people: tourist, Petr and me (cgy4ever). You can see that whatever handle is chosen, I must be the first, then tourist and Petr must be the last.
In example 3, if Copernicus uses "copernicus" as his handle, everything will be alright.