CF605E Intergalaxy Trips
Description
The scientists have recently discovered wormholes — objects in space that allow to travel very long distances between galaxies and star systems.
The scientists know that there are $ n $ galaxies within reach. You are in the galaxy number $ 1 $ and you need to get to the galaxy number $ n $ . To get from galaxy $ i $ to galaxy $ j $ , you need to fly onto a wormhole $ (i,j) $ and in exactly one galaxy day you will find yourself in galaxy $ j $ .
Unfortunately, the required wormhole is not always available. Every galaxy day they disappear and appear at random. However, the state of wormholes does not change within one galaxy day. A wormhole from galaxy $ i $ to galaxy $ j $ exists during each galaxy day taken separately with probability $ p_{ij} $ . You can always find out what wormholes exist at the given moment. At each moment you can either travel to another galaxy through one of wormholes that exist at this moment or you can simply wait for one galaxy day to see which wormholes will lead from your current position at the next day.
Your task is to find the expected value of time needed to travel from galaxy $ 1 $ to galaxy $ n $ , if you act in the optimal way. It is guaranteed that this expected value exists.
Input Format
The first line of the input contains a single integer $ n $ ( $ 1
Output Format
Print a single real value — the expected value of the time needed to travel from galaxy $ 1 $ to galaxy $ n $ if one acts in an optimal way. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed $ 10^{-6} $ .
Namely: let's assume that your answer is $ a $ , and the answer of the jury is $ b $ . The checker program will consider your answer correct, if 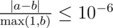.
Explanation/Hint
In the second sample the wormhole from galaxy $ 1 $ to galaxy $ 2 $ appears every day with probability equal to $ 0.3 $ . The expected value of days one needs to wait before this event occurs is 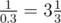.