CF730F Ber Patio
Description
Polycarp is a regular customer at the restaurant "Ber Patio". He likes having lunches there.
"Ber Patio" has special discount program for regular customers. A customer can collect bonuses and partially cover expenses in the restaurant.
Let's assume a customer currently has $ b $ bonuses and she has to pay $ r $ burles for a lunch. In this case the customer can use bonuses (1 bonus = 1 burle) to reduce the payment. She can cover at most half of the payment using bonuses. However, 1 bonus will be added to the customer's bonus balance per each 10 burles she paid.
Formally:
1. a customer can choose any number $ x $ of bonuses to use (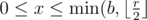)),
2. the customer's bonus balance is reduced by $ x $ ,
3. the customer pays $ r-x $ burles,
4. the customer's bonus balance is increased by $ ⌊(r-x)/10⌋ $ (i.e. integer division rounded down is used).
Initially, there are $ b $ bonuses on Polycarp's account. Polycarp is going to have a lunch in "Ber Patio" for the next $ n $ days. He estimated the values $ a_{1},a_{2},...,a_{n} $ , where $ a_{i} $ is the number of burles in a receipt for the $ i $ -th day. The sum over all receipts doesn't exceed $ 10^{5} $ burles.
Write a program to find the minimum number of burles Polycarp has to spend and an optimal strategy to use bonuses.
Input Format
The first line contains two integer numbers $ n $ and $ b $ ( $ 1
Output Format
On the first line, print the expected minimal number of burles to pay for all $ n $ receipts.
On the second line, print the sequence of integer numbers $ b_{1},b_{2},...,b_{n} $ , where $ b_{i} $ is the number of bonuses to use on the $ i $ -th day. If there are multiple solutions, print any of them.