CF772D Varying Kibibits
Description
You are given $ n $ integers $ a_{1},a_{2},...,a_{n} $ . Denote this list of integers as $ T $ .
Let $ f(L) $ be a function that takes in a non-empty list of integers $ L $ .
The function will output another integer as follows:
- First, all integers in $ L $ are padded with leading zeros so they are all the same length as the maximum length number in $ L $ .
- We will construct a string where the $ i $ -th character is the minimum of the $ i $ -th character in padded input numbers.
- The output is the number representing the string interpreted in base 10.
For example $ f(10,9)=0 $ , $ f(123,321)=121 $ , $ f(530,932,81)=30 $ .
Define the function
$$G(x)=x\cdot((\sum_{S\subseteq T,S\neq \varnothing,f(S)=x}(\sum_{y\in S}y)^2)\bmod (10^9+7))$$
$ %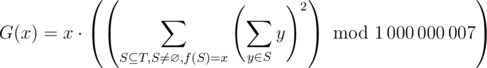 $
Here, $\subseteq$ denotes a subsequence.In other words, $ G(x) $ is the sum of squares of sum of elements of nonempty subsequences of $ T $ that evaluate to $ x $ when plugged into $ f $ modulo $ 1000000007 $ , then multiplied by $ x $ . The last multiplication is not modded.
You would like to compute $ G(0),G(1),...,G(999999) $ . To reduce the output size, print the value $G(0)\oplus G(1)\oplus G(2)\oplus \cdots\oplus G(999\,999)$, where $\oplus$ denotes the bitwise XOR operator.
Input Format
The first line contains the integer $ n $ ( $ 1
Output Format
Output a single integer, the answer to the problem.
Explanation/Hint
For the first sample, the nonzero values of $ G $ are $ G(121)=144611577 $ , $ G(123)=58401999 $ , $ G(321)=279403857 $ , $ G(555)=170953875 $ . The bitwise XOR of these numbers is equal to $ 292711924 $ .
For example, $G(123)=123\cdot((123^2+(123+555)^2)\bmod (10^9+7))=58\,401\,999$, since the subsequences $ [123] $ and $ [123,555] $ evaluate to $ 123 $ when plugged into $ f $ .
For the second sample, we have $G(999\,999)=999\,999\cdot(999\,999^2\bmod (10^9+7))$
For the last sample, we have $G(1)=\sum_{i=1}^{10}\binom{10}{i}i^2=28\,160$, where $10 \choose i$ is the binomial coefficient.