CF776G Sherlock and the Encrypted Data
Description
Sherlock found a piece of encrypted data which he thinks will be useful to catch Moriarty. The encrypted data consists of two integer $ l $ and $ r $ . He noticed that these integers were in hexadecimal form.
He takes each of the integers from $ l $ to $ r $ , and performs the following operations:
1. He lists the distinct digits present in the given number. For example: for $ 1014_{16} $ , he lists the digits as $ 1,0,4 $ .
2. Then he sums respective powers of two for each digit listed in the step above. Like in the above example $ sum=2^{1}+2^{0}+2^{4}=19_{10} $ .
3. He changes the initial number by applying bitwise xor of the initial number and the sum. Example: 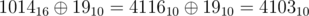. Note that xor is done in binary notation.
One more example: for integer 1e the sum is $ sum=2^{1}+2^{14} $ . Letters a, b, c, d, e, f denote hexadecimal digits $ 10 $ , $ 11 $ , $ 12 $ , $ 13 $ , $ 14 $ , $ 15 $ , respertively.
Sherlock wants to count the numbers in the range from $ l $ to $ r $ (both inclusive) which decrease on application of the above four steps. He wants you to answer his $ q $ queries for different $ l $ and $ r $ .
Input Format
First line contains the integer $ q $ ( $ 1
Output Format
Output $ q $ lines, $ i $ -th line contains answer to the $ i $ -th query (in decimal notation).
Explanation/Hint
For the second input,
$ 14_{16}=20_{10} $
$ sum=2^{1}+2^{4}=18 $
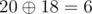
Thus, it reduces. And, we can verify that it is the only number in range $ 1 $ to $ 1e $ that reduces.