CF999E Reachability from the Capital
Description
There are $ n $ cities and $ m $ roads in Berland. Each road connects a pair of cities. The roads in Berland are one-way.
What is the minimum number of new roads that need to be built to make all the cities reachable from the capital?
New roads will also be one-way.
Input Format
The first line of input consists of three integers $ n $ , $ m $ and $ s $ ( $ 1 \le n \le 5000, 0 \le m \le 5000, 1 \le s \le n $ ) — the number of cities, the number of roads and the index of the capital. Cities are indexed from $ 1 $ to $ n $ .
The following $ m $ lines contain roads: road $ i $ is given as a pair of cities $ u_i $ , $ v_i $ ( $ 1 \le u_i, v_i \le n $ , $ u_i \ne v_i $ ). For each pair of cities $ (u, v) $ , there can be at most one road from $ u $ to $ v $ . Roads in opposite directions between a pair of cities are allowed (i.e. from $ u $ to $ v $ and from $ v $ to $ u $ ).
Output Format
Print one integer — the minimum number of extra roads needed to make all the cities reachable from city $ s $ . If all the cities are already reachable from $ s $ , print 0.
Explanation/Hint
The first example is illustrated by the following:
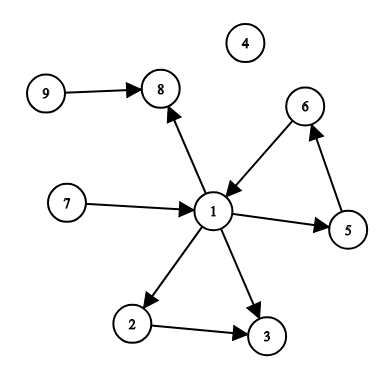For example, you can add roads ( $ 6, 4 $ ), ( $ 7, 9 $ ), ( $ 1, 7 $ ) to make all the cities reachable from $ s = 1 $ .
The second example is illustrated by the following:
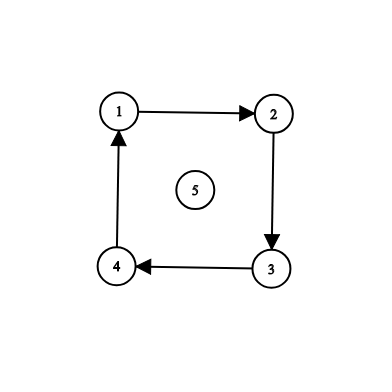In this example, you can add any one of the roads ( $ 5, 1 $ ), ( $ 5, 2 $ ), ( $ 5, 3 $ ), ( $ 5, 4 $ ) to make all the cities reachable from $ s = 5 $ .