P13011 【MX-X13-T6】"All I Can Do Is Quietly Wait for the Day When Fate Runs Out"
Background
When fate runs out and relationships break, will we still be together?
Description
For a permutation $p_{1\sim n}$, construct its **max-heap Cartesian tree**, then disconnect the edge between each node and its right child (if it exists). Denote the resulting forest as $T(p)$.
For example, consider $p_{1\sim 5} = [1, 3, 2, 5, 4]$. The max-heap Cartesian tree and $T(p)$ are shown below:
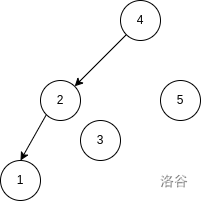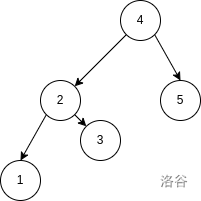
Given $n, x, y$, you need to determine how many of the $n!$ permutations of $1\sim n$ satisfy that nodes $x$ and $y$ belong to the same tree in $T(p)$. **Nodes are identified by their indices, not their values in $p$.**
Since the answer may be large, output it modulo a prime $P$.
Input Format
**This problem contains multiple test cases.**
The first line contains two positive integers $T$ and $P$, representing the number of test cases and the modulo. **It is guaranteed that $\bm{P}$ is a prime.** For each test case:
- One line with three positive integers $n, x, y$.
Output Format
For each test case, output a non-negative integer indicating the number of valid permutations modulo $P$.
Explanation/Hint
### Sample Explanation
For the first test case, the following $6$ permutations satisfy the condition:
$[1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 3, 2, 4], [2, 1, 3, 4], [2, 3, 1, 4], [3, 1, 2, 4], [3, 2, 1, 4]$.
For the second test case, all $1\sim 4$ permutations are valid.
### Constraints
**This problem uses bundling tests.**
| Subtask | Points | $n\leq$ | $T\leq$ | Special Constraints |
|:------:|:------:|:------:|:------:|:------------------:|
| $1$ | $5$ | $8$ | $10^6$ | None |
| $2$ | $15$ | $2000$ | $2000$ | None |
| $3$ | $15$ | $2000$ | $10^6$ | None |
| $4$ | $25$ | $5\times10^6$ | $20$ | None |
| $5$ | $15$ | $10^5$ | $10^6$ | A |
| $6$ | $25$ | $5\times10^6$ | $10^6$ | None |
- Special Constraint A: $P=998244353$.
For all test cases:
- $1 \leq T \leq 10^6$,
- $1 \le x, y \le n \le 5 \times 10^6$,
- $10^8 \le P \le 10^9 + 7$ and $P$ is a prime.
### Hint
Please use a fast input method.
---
*Translation by DeepSeek V3.*