P14669 [ICPC 2025 Seoul R] Bay
Description
We have a grid (lattice) graph $G(n, n)$, where $n$ is the number of vertices along both the $x$-axis and the $y$-axis, that is, the number of rows and columns. The vertices of the graph $G(n, n)$ are numbered consecutively from 1 to $n^2$ in row-major ordering; starting from the top-left vertex, we traverse row by row from top to bottom, and within each row from left to right. Figure 1 shows two examples, $G(5, 5)$ and $G(7, 7)$ with vertex numbers.
:::align{center}
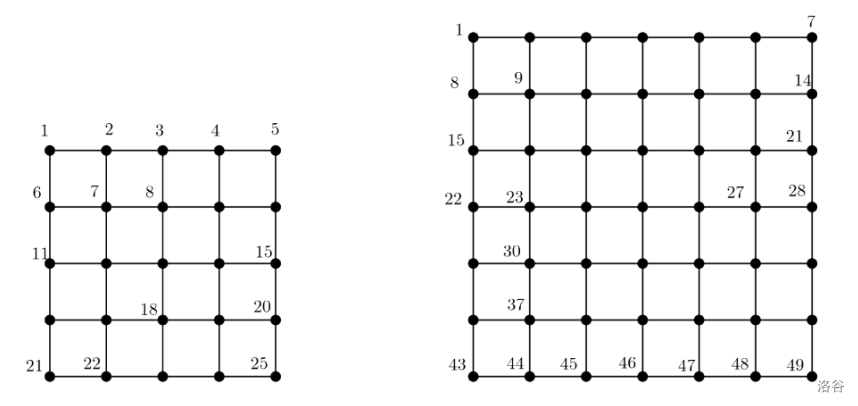
Figure 1. Left: Grid graph $G(5, 5)$. Right: $G(7, 7)$.
:::
We are given a spanning tree $T$ of $G(n, n)$. The left in Figure 2 shows a spanning tree $T$ of $G(7, 7)$. If we add an edge of $G(n, n)$ that does not belong to $T$ (called non-tree edge), then exactly one simple cycle is created. We define the region enclosed by this cycle as a *bay*. There is a one-to-one correspondence between non-tree edges and bays, that is, each non-tree edge corresponds to exactly one bay. The area of a bay is defined by number of $1 \times 1$ unit cells enclosed by the cycle. The right in Figure 2 shows two bays (colored blue and orange) created by adding two non-tree edges $(u, v)$ and $(p, q)$, respectively. Note that the areas of two bays created by $(u, v)$ and $(p, q)$ are 4 and 12, respectively.
:::align{center}
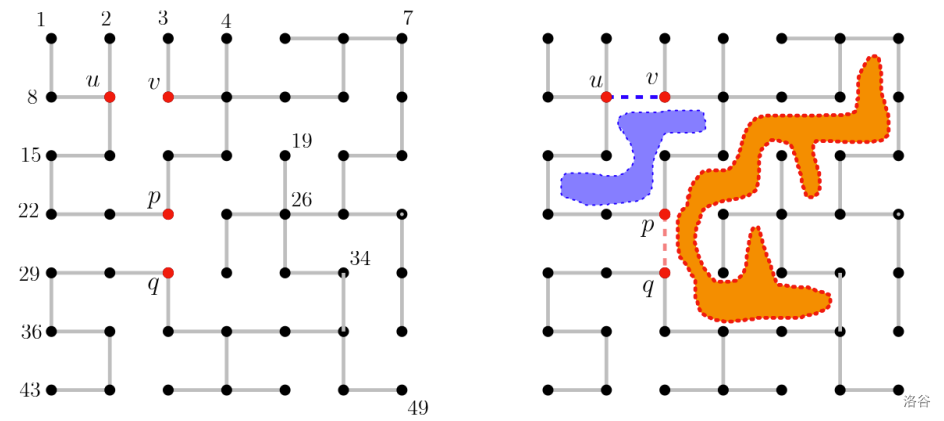
Figure 2. A spanning tree $T$ of a grid $G(7, 7)$ and two bays created by $(u, v)$ and $(p, q)$.
:::
Given a spanning tree $T$ of a grid graph $G(n, n)$ and a positive integer $S$, write a program that finds all non-tree edges that creates bays of area $S$ and outputs the first non-tree edge among them in lexicographical order.
Input Format
Your program is to read from standard input. The input starts with a line containing two integers $n$ and $S$ where $5 \le n \le 300$ for $G(n, n)$ and $1 \le S \le (n-1)^2$. Each of the following $n^2 - 1$ lines contains two distinct integers $u$ and $v$ representing an edge $(u, v)$ of a spanning tree $T$, where $1 \le u < v \le n^2$.
Output Format
Your program is to write to standard output. The first line should contain the number of non-tree edges that create the bays of area $S$. The second line should contain two distinct integers $u$ and $v$ ($u < v$) representing the first non-tree edge $(u, v)$ in lexicographical order among those that create the bays of area $S$. The lexicographical order of two edges $(a, b)$ and $(c, d)$ is defined such that $(a, b)$ comes before $(c, d)$ if and only if $a < c$ or $a = c$ then $b < d$. If there is no non-tree edge that creates the bay of area $S$, then print "0" in the first line and two zeros "0 0" in the second line.
Figure 3 shows two spanning trees of a grid graph with $n = 5$, which are the sample inputs and outputs.
:::align{center}
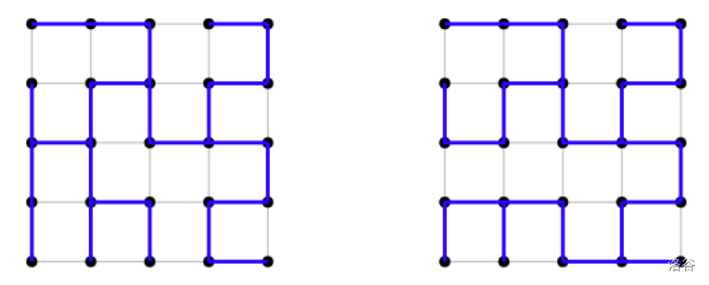
Figure 3. Two spanning trees of $G(5, 5)$ for Sample Input 1 and 2
:::