P14819 [ICPC 2023 Yokohama R] Color Inversion on a Huge Chessboard
Description
You are given a set of square cells arranged in a chessboard-like pattern with $n$ horizontal rows and $n$ vertical columns. Rows are numbered 1 through $n$ from top to bottom, and columns are also numbered 1 through $n$ from left to right.
Initially, the cells are colored as in a chessboard, that is, the cell in the row $i$ and the column $j$ is colored black if $i + j$ is odd and is colored white if it is even.
Color-inversion operations, each of which is one of the following two, are made one after another.
**Invert colors of a row**: Given a row number, invert colors of all the cells in the specified row. The white cells in the row become black and the black ones become white.
**Invert colors of a column**: Given a column number, invert colors of all the cells in the specified column. The white cells in the column become black and the black ones become white.
The number of distinct **areas** after each of the operations should be counted. Here, an area means a group of directly or indirectly connected cells of the same color. Two cells are said to be directly connected when they share an edge.
Input Format
The input consists of a single test case of the following format.
$$\begin{aligned}
&n\ q \\
&operation_1 \\
&\vdots \\
&operation_q
\end{aligned}$$
The integer $n$ is the number of rows and columns ($1 \leq n \leq 5 \times 10^5$). The integer $q$ is the number of operations ($1 \leq q \leq 5 \times 10^5$). The following $q$ lines represent operations to be made in this order. Each of them is given in either of the following forms.
- **ROW $i$**: the operation “invert colors of a row” applied to the row $i$ ($1 \leq i \leq n$).
- **COLUMN $j$**: the operation “invert colors of a column” applied to the column $j$ ($1 \leq j \leq n$).
Output Format
Output $q$ lines. The $k$-th line should contain an integer denoting the number of areas after the $k$-th operation is made.
Explanation/Hint
:::align{center}
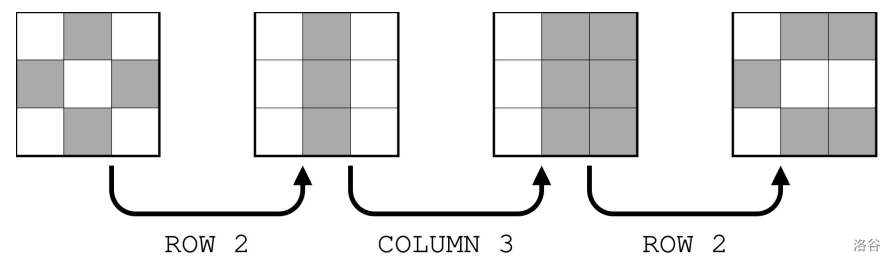
Figure F.1. Illustration of Sample Input 1
:::