P1772 [ZJOI2006] Logistics Transportation
Description
A logistics company needs to transport a batch of goods from port A to port B. Because the amount of goods is large, it will take $n$ days to finish. In general, the goods need to be transferred through several intermediate ports.
The company usually designs a fixed transportation route to enable strict management and tracking. Due to various factors, sometimes a port cannot load or unload cargo. In such cases, the route must be modified so that the goods can arrive on time.
However, changing the route is troublesome and incurs extra cost. Therefore, the company wants to make a transportation plan for $n$ days that minimizes the total cost.
On each day, you must choose a valid route from port A to port B that does not pass through any port that is unavailable on that day. Each time the route differs from the previous day’s route, an additional cost of $k$ is incurred. The transportation fee per unit length is $1$. Ports are numbered from $1$ to $m$, where port A is $1$ and port B is $m$. All shipping routes are bidirectional. It is guaranteed that on every day there is at least one valid route from A to B.
The goal is to minimize the total cost, which equals the sum of the route lengths over $n$ days plus $k \times$ the number of times the route is changed.
Input Format
The first line contains four integers $n, m, k, e$, where $n$ is the number of days, $m$ is the number of ports, $k$ is the cost of changing the route, and $e$ is the number of shipping routes.
Each of the next $e$ lines contains three integers $u, v, w$, meaning there is a bidirectional shipping route between ports $u$ and $v$ with length $w$. The transportation fee per unit length is $1$. Port A is numbered $1$, and port B is numbered $m$.
The next line contains an integer $d$. Each of the following $d$ lines contains three integers $p, a, b$, meaning port $p$ is unavailable during days $[a, b]$ (inclusive). The same port may be unavailable during multiple time intervals. For every day, there exists at least one route from port A to port B.
Output Format
Output a single integer: the minimal total cost.
The total cost is the sum of route lengths over $n$ days $+\, k \times$ the number of times the route is changed.
Explanation/Hint
Constraints
For $100\%$ of the testdata, $1 \le n \le 100$, $1 \le m \le 20$, $1 \le k \le 500$, $1 \le e \le 200$.
Sample Input Explanation
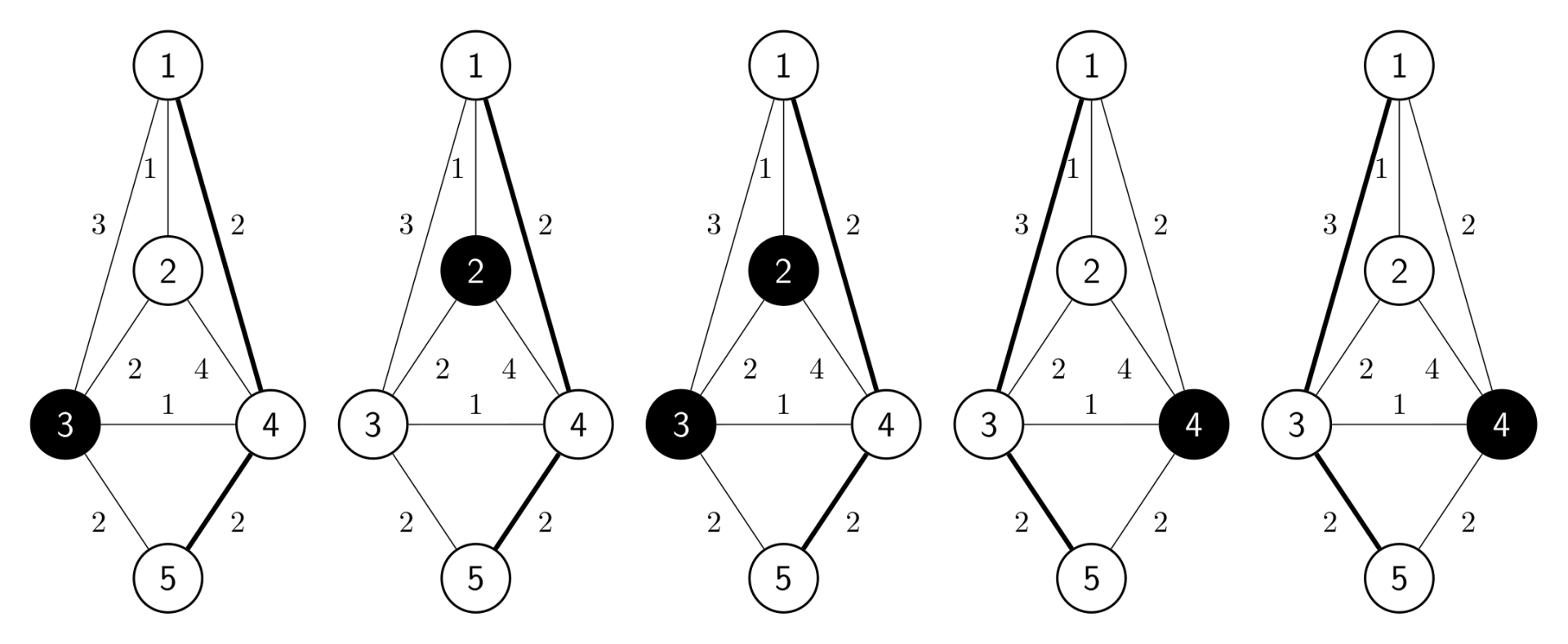
The figure shows the situations from day $1$ to day $5$; shaded ports are unavailable.
Sample Output Explanation
Use route $1 \to 4 \to 5$ for the first three days, and route $1 \to 3 \to 5$ for the last two days. Then the total cost is $(2+2) \times 3 + (3+2) \times 2 + 10 = 32$.
Source: NOI Guide 2010 Senior (01).
Translated by ChatGPT 5