P3220 [HNOI2012] NAND
Background
If you can provide the full statement or a brief description of the problem, please post it directly in the discussion area. Thank you for your contribution.
Description
NAND is a binary logical operation whose result is true if and only if the two input Boolean values are not both true. The truth table of the NAND operation is as follows (1 denotes true, 0 denotes false):
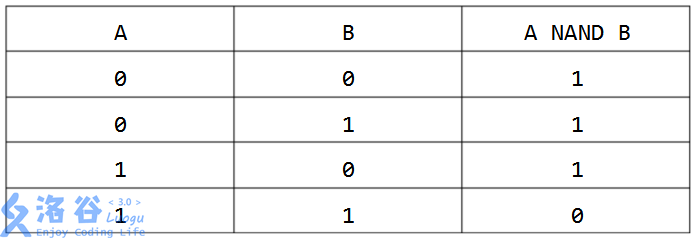
The NAND of two non-negative integers means writing them in binary and then applying the NAND operation bitwise on corresponding binary digits. Since the lengths of the two binary numbers may differ, we generally fix a most significant bit limit $K$ so that the binary representations of both numbers do not exceed $K$ bits; numbers shorter than $K$ bits are padded with leading zeros on the left.
Given $N$ non-negative integers $A_1, A_2, \ldots, A_N$ and the designated bit-length $K$, using NAND operations and parentheses, where each number may be used any number of times, please determine how many numbers in the range $[L, R]$ can be obtained.
Input Format
The first line contains four positive integers $N$, $K$, $L$, and $R$ separated by spaces.
The second line contains $N$ non-negative integers $A_1, A_2, \ldots, A_N$, as described above.
Constraints: $K \le 60$ and $N \le 1000$, $0 \le A_i \le 2^K - 1$, $0 \le L \le R \le 10^{18}$.
Output Format
Output a single integer, the number of values in $[L, R]$ that can be computed.
Explanation/Hint
In Sample 1, $(3 \text{ NAND } 4) \text{ NAND } (3 \text{ NAND } 5) = 1$, $5 \text{ NAND } 5 = 2$, and $3$ and $4$ can be obtained directly.
Translated by ChatGPT 5