P3770 [CTSC2017] Key
Description
A key is a string of length $n = 2k + 1$ that contains 1 letter X, $k$ letters A, and $k$ letters B. For example, when $k = 3$, BAXABAB is a key.
As shown in the figure below, these $2k + 1$ letters can be arranged in a circle in clockwise order:
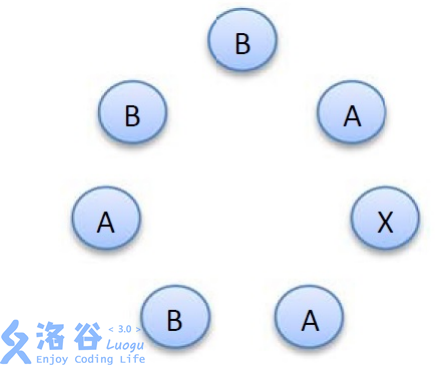
Among the $k$ letters A, some can be defined as "strong". Specifically, starting from X and walking clockwise to some A, if along the way the number of A is strictly greater than the number of B, then that letter A is called strong.
In the above example, the 1st and 2nd letters A counted clockwise from X are strong, while the 3rd letter A is not strong.
The characteristic value of a key is the number of strong letters A it contains.
The genius child KT gave the following result:
Assume the positions of the $k$ letters A are fixed, but the positions of the remaining $k$ letters B and 1 letter X are unknown. (Note that there are exactly $k + 1$ keys that meet this condition, because X still has $k + 1$ possible positions.)
It can be proved that the characteristic values of all these $k + 1$ possible keys are pairwise distinct and are exactly $0, 1, 2, \dots, k$.
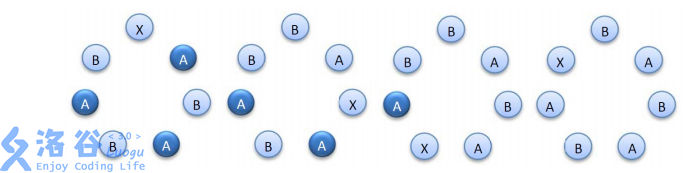
The following figure is a concrete example. From left to right, the four sub-figures have 3, 2, 1, and 0 strong letters A, respectively.
Similarly, if the positions of the $k$ letters B are fixed, then the characteristic values of all $k + 1$ keys that meet the condition are also pairwise distinct and are exactly $0, 1, \dots, k$.
Now you need to solve the following three problems:
1. Given the positions of all A in the key, when the characteristic value is $0$, where is X located?
2. Given the positions of all A in the key, when the characteristic value is $S$, where is X located?
3. Given the positions of all B in the key, when the characteristic value is $S$, where is X located?
Note: The positions of the $2k + 1$ letters of the string are numbered from $1$ to $2k + 1$.
[Example 1]
Assume $k = 3$, $S = 2$. Then:
- When the positions of A are {2, 4, 6} and the characteristic value is $0$, the position of X is $7$.
- When the positions of A are {2, 4, 6} and the characteristic value is $2$, the position of X is $3$.
- When the positions of B are {2, 4, 6} and the characteristic value is $2$, the position of X is $5$.
[Example 2]
Assume $k = 9$, $S = 7$. Then:
- When the positions of A are {3, 4, 5, 9, 10, 12, 13, 16, 19} and the characteristic value is $0$, the position of X is $14$.
- When the positions of A are {3, 4, 5, 9, 10, 12, 13, 16, 19} and the characteristic value is $7$, the position of X is $18$.
- When the positions of B are {3, 4, 5, 9, 10, 12, 13, 16, 19} and the characteristic value is $7$, the position of X is $17$.
Input Format
There is only one set of testdata.
The first line contains an integer $k$, as described above.
The second line contains an integer seed, which will be used to generate a $k$-element set $P$.
The third line contains an integer $S$, as described above.
It is guaranteed that $0 \le S \le k \le 10^7$. $1 \le \text{seed} \le 10000$.
Under cipher/, there are two files for generating the input data, cipher.cpp/pas. The reading part has been completed. In the array $p[]$, if $p[i] = 0$, it means $i$ is not in set $P$; otherwise, $i$ is in set $P$.
[Baidu Netdisk link>> Password: 9vr3](http://pan.baidu.com/s/1i55NdWx) Please compile it yourself.
```cpp
#include
#include
int p[20000005];
int seed, n, k, S;
int getrand() {
seed = ((seed * 12321) ^ 9999) % 32768;
return seed;
}
void generateData() {
scanf( "%d%d%d", &k, &seed, &S );
int t = 0;
n = k * 2 + 1;
memset(p, 0, sizeof(p));
for( int i = 1; i k ) {
while ( p[i] == 0 ) ++i;
p[i] = 0;
--t;
}
while( t < k ) {
while( p[i] == 1 ) ++i;
p[i] = 1;
++t;
}
}
int main() {
generateData();
return 0;
}
```
Output Format
Output three lines, one number per line, corresponding to the answers to the three subproblems in the description.
That is:
1. The first number indicates the position of X when the $k$-element set $P$ represents the positions of A and the characteristic value is $0$.
2. The second number indicates the position of X when the $k$-element set $P$ represents the positions of A and the characteristic value is $S$.
3. The third number indicates the position of X when the $k$-element set $P$ represents the positions of B and the characteristic value is $S$.
Explanation/Hint
[Sample Explanation]
In the first sample, the indices of elements where array $P$ is $1$ are $5, 6, 7, 8, 9$.
[Constraints and Conventions]
- For 30% of the testdata, $k \le 10^3$.
- For 50% of the testdata, $k \le 10^5$.
- For 100% of the testdata, $k \le 10^7$.
For each test point, the score is the sum of the following three parts:
1. If you answer the first question correctly, you will get 3 points.
2. If you answer the second question correctly, you will get 4 points.
3. If you answer the third question correctly, you will get 3 points.
If you only know part of the answers, please still output three numbers in this required format. Otherwise, you may lose points due to formatting errors.
Translated by ChatGPT 5