P3939 Counting Colors
Background
Large samples can be downloaded from “Attachments” at the bottom of the page.
Description
Xiao C’s rabbits are not snow-white, but colorful. Each rabbit has a color, and different rabbits may share the same color. Xiao C lines up her $n$ rabbits, numbered from $1$ to $n$, in a long row to feed them carrots. After arranging, the color of the $i$-th rabbit is $a_i$.
As the saying goes, “Different strokes for different folks.” Xiao C finds that rabbits of different colors may have different preferences for carrots. For example, silver rabbits like golden carrots the most, golden rabbits prefer carrot leaves, while green rabbits like sour carrots... To satisfy the rabbits’ needs, Xiao C is quite troubled. Therefore, to feed carrots more accurately, Xiao C wants to know how many rabbits of color $c_j$ are in the interval $[l_j, r_j]$.
However, Xiao C’s rabbits are very active and are not willing to stay in fixed positions; meanwhile, Xiao C also rearranges the rabbits based on what she knows. So, sometimes the rabbits numbered $x_j$ and $x_j + 1$ will swap positions. Xiao C is overwhelmed by this series of hassles. Can you help her?
Input Format
Read from standard input. The first line contains two positive integers $n, m$.
The second line contains $n$ positive integers; the $i$-th number denotes the color $a_i$ of the $i$-th rabbit.
The next $m$ lines each describe one of the following two types of operations:
- “$1\ l_j\ r_j\ c_j$”: Query how many rabbits of color $c_j$ are in the interval $[l_j, r_j]$.
- “$2\ x_j$”: The rabbits numbered $x_j$ and $x_j + 1$ swap positions.
Output Format
Print to standard output.
For each type-1 operation, output one positive integer on a separate line, which is the answer to that query.
Explanation/Hint
[Sample 1 Explanation]
The first two type-1 operations and the last two type-1 operations are the same queries. After the third type-2 operation, rabbit $3$ and rabbit $4$ swap positions, and the sequence becomes 1 2 2 3 3 3.
[Constraints]
Subtasks provide characteristics of partial testdata. If you encounter difficulties, you can try to solve only part of the testdata. For all test points, $1 \le l_j < r_j \le n$, $1 \le x_j < n$. The scale and characteristics of each test point are shown in the following table:
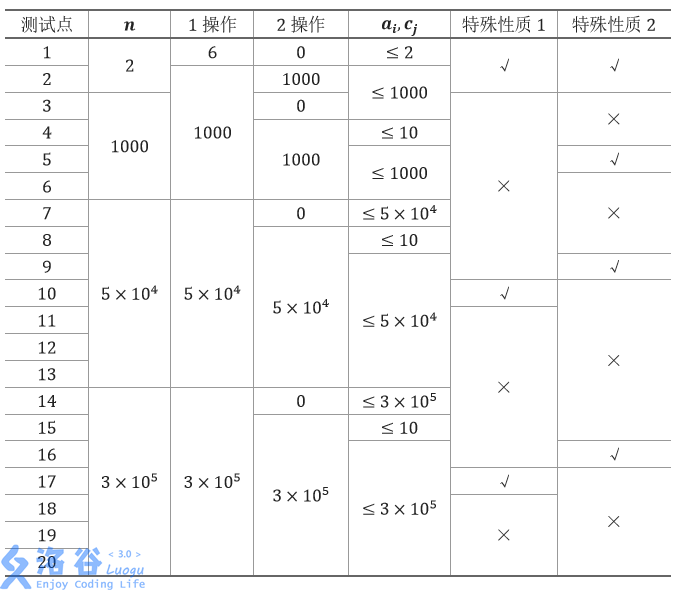
Special Property 1: For all type-1 operations, it is guaranteed that either $|r_j - l_j| \le 20$ or $|r_j - l_j| \le n - 20$.
Special Property 2: It is guaranteed that no two rabbits have the same color.
Translated by ChatGPT 5