P3958 [NOIP 2017 Senior] Cheese
Background
NOIP 2017 Senior D2T1.
Description
There is a large block of cheese with height $h$, and we may regard its length and width as infinite. Inside the cheese, there are many spherical cavities with the same radius. We can establish a 3D coordinate system in the cheese, where the bottom surface of the cheese is $z = 0$ and the top surface is $z = h$.
Now, there is a little mouse Jerry on the bottom surface of the cheese. He knows the coordinates of the centers of all the cavities. If two cavities are tangent to or intersect each other, then Jerry can run from one cavity to the other. In particular, if a cavity is tangent to or intersects the bottom surface, Jerry can enter the cavity from the bottom surface; if a cavity is tangent to or intersects the top surface, Jerry can go from the cavity to the top surface.
Starting on the bottom surface, Jerry wants to know whether he can reach the top surface by using the existing cavities without damaging the cheese.
The distance between two points $P_1(x_1, y_1, z_1)$ and $P_2(x_2, y_2, z_2)$ in space is:
$$\mathrm{dist}(P_1,P_2)=\sqrt{(x_1-x_2)^2+(y_1-y_2)^2+(z_1-z_2)^2}.$$
Input Format
Each input file contains multiple data sets.
The first line contains a positive integer $T$, the number of data sets in the file.
Then follow $T$ data sets, each with the following format: The first line contains three positive integers $n, h, r$, separated by a space, representing the number of cavities, the height of the cheese, and the radius of each cavity.
The next $n$ lines each contain three integers $x, y, z$, separated by a space, indicating that the center of a cavity is at $(x, y, z)$.
Output Format
Output $T$ lines. For the $i$-th data set, if Jerry can go from the bottom surface to the top surface, output `Yes`; otherwise, output `No`.
Explanation/Hint
【Explanation for Sample I/O 1】
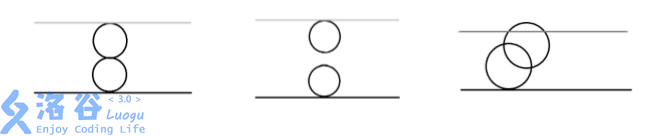
For the first data set, from the cross-sectional view:
- The first cavity is tangent to the bottom surface at $(0, 0, 0)$.
- The second cavity is tangent to the top surface at $(0, 0, 4)$.
- The two cavities are tangent at $(0, 0, 2)$.
Output `Yes`.
For the second data set, from the cross-sectional view:
- The two cavities neither intersect nor are tangent.
Output `No`.
For the third data set, from the cross-sectional view:
- The two cavities intersect, and they are each tangent to or intersect the top and bottom surfaces.
Output `Yes`.
【Constraints】
- For $20\%$ of the testdata, $n = 1$, $1 \le h, r \le 10^4$, and the absolute value of each coordinate does not exceed $10^4$.
- For $40\%$ of the testdata, $1 \le n \le 8$, $1 \le h, r \le 10^4$, and the absolute value of each coordinate does not exceed $10^4$.
- For $80\%$ of the testdata, $1 \le n \le 10^3$, $1 \le h, r \le 10^4$, and the absolute value of each coordinate does not exceed $10^4$.
- For $100\%$ of the testdata, $1 \le n \le 1 \times 10^3$, $1 \le h, r \le 10^9$, $1 \le T \le 20$, and the absolute value of each coordinate does not exceed $10^9$.
Translated by ChatGPT 5