P4386 [SHOI2015] Parts Assembly Machine
Description
SHTSC, the inventor who once created a laser generator, has now unveiled his new invention: the Parts Assembly Machine — a mysterious device that can produce and assemble parts.
A part is an undirected graph whose vertices are labeled from $0$ to $n-1$, and the machine has the following two functions:
1. Produce a part that has only one vertex labeled $0$ and no edges.
2. Combine two existing parts $G_1$ and $G_2$, with the number of vertices of $G_2$ being $m$ and greater than or equal to the number of vertices of $G_1$, which is $n$, to obtain a new part $G$. The vertex set of $G$ is the union of the vertex sets of $G_1$ and $G_2$, and vertex $i(0\leq i < m)$ of $G_2$ is relabeled as $n+i$. The edge set of $G$ is the union of the edge sets of $G_1$ and $G_2$, then for every vertex with label $a(a \geq n)$, add an undirected edge connecting $(a,a \bmod n)$.
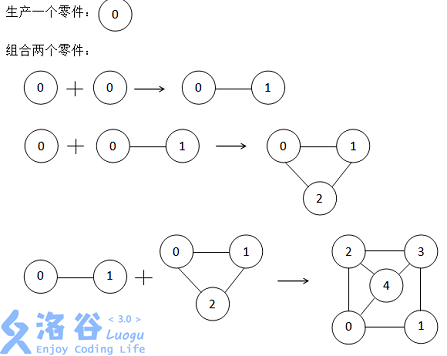
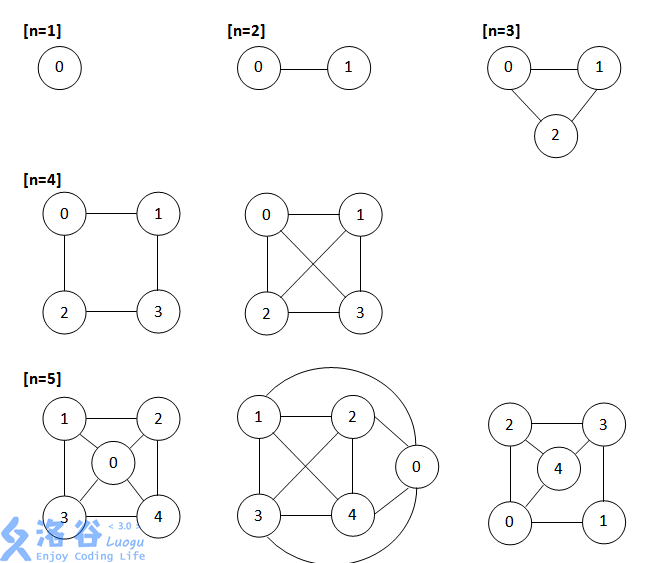
Now SHTSC is wondering whether a given part can be produced by the machine. Note that parts are labeled, which means two parts are considered different even if they only differ by labels. To help you understand the problem, SHTSC has provided diagrams of all parts with number of vertices $\le 5$.
Input Format
The first line contains an integer $t$, the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains two integers $n$ and $m$, indicating a labeled undirected graph with $n$ vertices labeled from $0$ to $n - 1$ and $m$ edges. Then $m$ lines follow, each containing two integers $u,v$, representing an undirected edge between $u$ and $v$.
Output Format
For each test case, output one line. If the undirected graph can be produced by the Parts Assembly Machine, output `YES`; otherwise, output `NO`.
Explanation/Hint
For $5\%$ of the testdata, the given graph is connected and $m = n - 1$.
For another $15\%$ of the testdata, $n \leq 5$.
For $50\%$ of the testdata, $n \leq 1000$.
For all test points, $t \leq 10$, $n, m \leq 100000$.
Translated by ChatGPT 5