P4485 [BJWC2018] Topological Sequence
Description
Xiao C recently learned about topological sorting. Performing a topological sort on a directed acyclic graph $G$ means arranging all vertices of $G$ into a linear order such that for any directed edge $(u, v)$ in $G$, $u$ appears before $v$ in the linear order. For example, if the vertex set of $G$ is $\{1,2,3,4\}$ and the edge set is $\{(1,2)
,(1,3),(2,4),(3,4)\}$, then $(1,2,3,4)$ and $(1,3,2,4)$ are both topological sequences of $G$.
Now Xiao C performed a topological sort on a simple (no multiple edges) directed acyclic graph, but accidentally lost the original graph. Besides the topological sequence, he only remembers that the original graph has $k$ edges, and that there exists a vertex $u$ that can reach all other vertices in the graph. He wants to know how many simple directed acyclic graphs satisfy the above requirements. Since the answer may be large, you only need to output the answer modulo $m$.
Input Format
The first line contains three integers $n, k, m$.
The second line contains $n$ space-separated positive integers $a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n$, representing a topological sequence of the original graph, guaranteed to be a permutation of $1$ to $n$.
Output Format
Output a single integer, the remainder modulo $m$ of the number of simple directed acyclic graphs that satisfy the requirements.
Explanation/Hint
【Sample Explanation】
There are $9$ simple directed acyclic graphs that satisfy the requirements. Their edge sets are:
$\{(1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 3)\}$
$\{(1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 4)\}$
$\{(1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (3, 4)\}$
$\{(1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 3), (2, 4)\}$
$\{(1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 3), (3, 4)\}$
$\{(1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 4), (3, 4)\}$
$\{(1, 2), (1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 4)\}$
$\{(1, 2), (1, 4), (2, 3), (3, 4)\}$
$\{(1, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (3, 4)\}$
Constraints
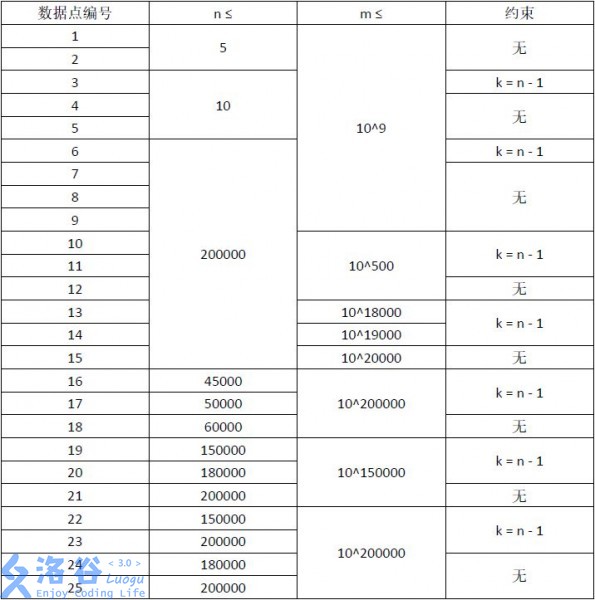
For $100\%$ of the testdata, $0 \le k \le n \le 2 \times 10^5$, $1 \le m \le 10^{200000}$.
Translated by ChatGPT 5