P4803 [CCO 2015] Solar Flight
Background
**Warning: abusing the judging system for this problem will result in your account being banned.**
Description
**This problem is translated from [CCO 2015](https://cemc.math.uwaterloo.ca/contests/computing/2015/index.html) Day 1 T3 “[Solar Flight](https://cemc.math.uwaterloo.ca/contests/computing/2015/stage%202/day1.pdf)”.**
A new era of aviation is coming—the first solar-powered giant jet airliner is about to enter commercial service. However, the public has some safety concerns about cutting-edge technology, because the sunlight that powers the plane may be blocked by other objects in the sky. Therefore, some statistics and calculations must be done first to plan the first flight.
We consider a graph consisting of $N$ air routes from one city to another. An airplane can be regarded as a point. The sky it travels through can be modeled as a Cartesian coordinate system, where the $X$ axis represents the distance eastward from any point, and the $Y$ axis represents altitude. We only consider $x$ values in the range $[0,X]$, and all routes are straight line segments. Plane $i$ flies from $(0,A_i)$ to $(X,B_i)$. All $A$ values are distinct, and all $B$ values are also distinct. Planes move along their routes at an unknown, possibly non-constant speed, so at any time, a plane may be at any position on its route. However, it is known that planes never collide with each other, so if two routes intersect, the two planes will never reach the intersection point at the same time.
Each plane $i$ also has an interference value $C_i$, which represents how strongly a plane affects the solar energy absorption of planes below it.
The solar panels on each plane are very strange: they can only collect energy directly above the plane. This means that the sunlight a plane can absorb may be blocked by other planes that have the same $x$ value but a larger $y$ value. Specifically, the amount by which the absorbed sunlight is reduced equals the sum of the interference values of the planes blocking it.
Given this information and a distance constant $K$, you need to answer $Q$ queries about possible effects on the solar panels. Query $i$ asks for the reduction in absorbed sunlight for plane $P_i$ at some moment, where at that moment the plane’s $x$ value lies within $[S_i,S_i+K]$.
Input Format
The first line contains four integers $X,K,N,Q$, representing the maximum $x$ value considered, the distance constant, the total number of routes, and the number of queries.
The next $N$ lines each contain three integers $A_i,B_i,C_i(1\le i \le N)$, representing plane $i$’s starting $y$ value, ending $y$ value, and interference value.
The next $Q$ lines each contain two integers $P_i, S_i(1\le i \le Q)$, meaning you should answer the question described above based on $P_i$ and $S_i$.
Output Format
Output $Q$ lines. Each line contains one integer: the answer to query $i(1\le i \le Q)$.
Explanation/Hint
A diagram of the flight routes is shown below.
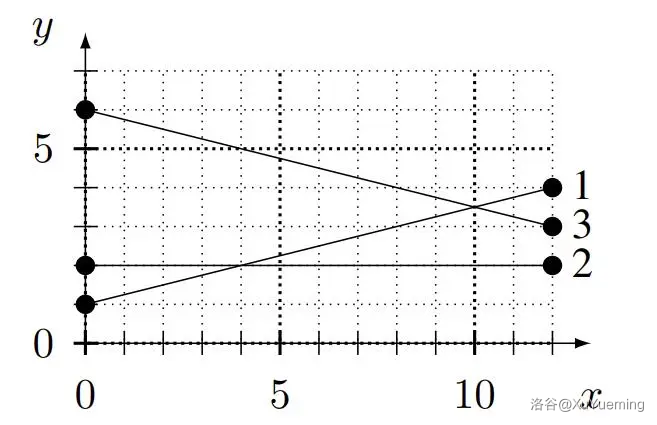
Query $1$ asks about plane $2$ within the range $[1,5]$. When the plane is at $x\le 4$, it may be blocked by plane $3$, but never by plane $1$. However, when $x>4$, it may be blocked by all other planes. Therefore, the answer to this query is the sum of the interference values of all other planes, which is $5+6=11$.
For query $2$, when $x