P5129 Incredible Maze.
Background
After merging powerful equipment, of course you have to explore the maze.
Description
However, when you were happily crushing enemies with a set of divine gear, Lady Keine cast a forgetting skill on you. As a result, without merging the "Ki" mark, you forgot the structure of the maze.
Since before forgetting you already knew this maze inside out, you do know that the $n$ rooms in this maze are all connected to each other, and there are $n$ roads connecting these rooms (of course, each road can be traveled in both directions).
Even in the incredible Gensokyo, basic common sense still exists. That is, there will not be a road connecting two identical rooms, and there will not be a road whose two ends are the same room.
After forgetting the maze structure, you have no way to know where you are, nor where the passage to the next floor is. Fortunately, you kept a rough map of this maze, so you know which two rooms each of these $n$ roads connects, as well as the length of each road.
To clear the level, you will go from your current position (a random location) to the passage to the next floor (also a random location) without traversing any road more than once. Obviously, there may be more than $1$ such path, and in that case you will randomly choose one of them.
Now you want to know the expected length of the path you walk. To avoid precision errors, you only need to take the result modulo $19260817$.
Input Format
The first line contains an integer $n$, indicating the number of rooms and the number of roads.
The next $n$ lines each contain three integers $u, v, w$, indicating that there is a road of length $w$ between room $u$ and room $v$.
Output Format
Output one integer on one line, representing the expected path length.
Explanation/Hint
#### Sample Explanation:
The structure of the maze is as follows:
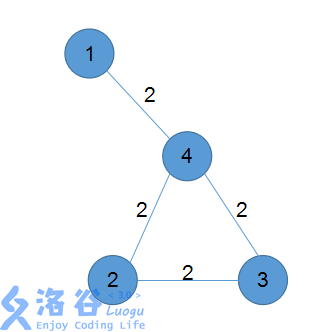
Both the start point and the end point are random, represented by an ordered pair $(x, y)$.
Take a few representative ordered pairs as examples:
$(1,1)$: there is only one path of length $0$.
$(1,2)$: there are two paths $1-4-2$ and $1-4-3-2$, and the expected path length is $\frac{4+6}{2}=5$.
$(3,3)$: there are two paths $3-2-4$ and $3$, and the expected path length is $\frac{6+0}{2}=3$.
It is not hard to calculate that the sum of the expected path lengths over all possible ordered pairs is $57$, so the answer is $\frac{57}{16}$, which equals $8426611$ under modulo arithmetic.
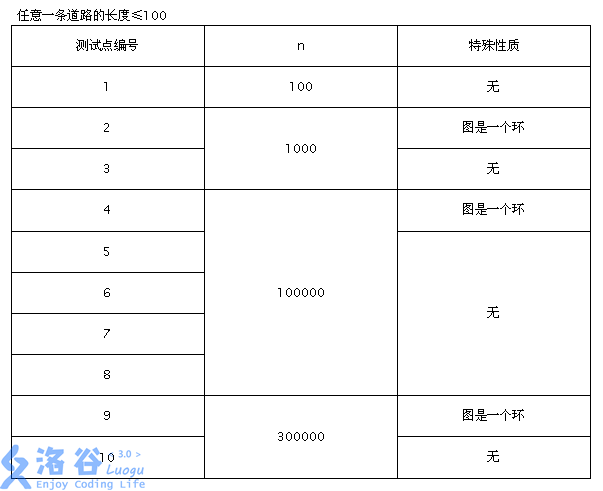
#### Constraints:
Translated by ChatGPT 5