P6272 [Hubei Provincial Team Mutual Test 2014] Arithmetic Without People
Background
Source: Week 1 of the 2014 Hubei Provincial Team Mutual Test.
Resource link: [Link](https://tieba.baidu.com/p/3050650090?red_tag=3002680446).
Description
Before everything began, the universe was boundless chaotic darkness, with only the spirit of God moving through it.
God was very dissatisfied with this endless darkness, so he waved his hand and said, “Let there be light,” and thus there was light in the world. From then on, there was the alternation of day and night. This was the first day of creation.
On the second day, God was still not satisfied with the empty scene before him, so he waved his hand and said, “Let there be zero.” Thus the first number appeared: $0$.
On the third day, God was very dissatisfied with having only $0$, so he waved his hand and said, “Let there be non-zero numbers.” Then God began to create new numbers. Each new number is represented by an ordered pair of numbers that have already been created, that is:
$$
x = (x_L, x_R)
$$
Thus, numbers such as $(0, 0), (0, (0, 0)), ((0, 0), 0), ((0, 0), (0, 0)), \cdots$ appeared. At night, all kinds of strange numbers galloped across the land.
(Note: these “numbers” created by God are different from ordinary natural numbers or rational numbers. They are recursively defined as described above. They are always pairs of numbers, and if you keep splitting them, you will eventually reach the indivisible $0$.)
On the fourth day, God saw that the numbers were indistinguishable from one another, so he waved his hand and said, “Let there be distinction.” Thus, in order to distinguish each number, God defined equality:
1. $0 = 0$.
2. For any $x_L, x_R, y_L, y_R$, if $x_L = y_L$ and $x_R = y_R$, then $(x_L, x_R) = (y_L, y_R)$.
3. For any $x, y$, $x = y$ if and only if one of the above conditions holds. Otherwise, write $x \not = y$.
On the fifth day, God saw the numbers in a complete mess, so he waved his hand and said, “Let there be order.” Thus, in order to compare numbers, God defined “less than”:
1. For any $x$, if $x \not = 0$, then $0 < x$.
2. For any $x_L, x_R, y_L, y_R$, if $x_L < y_L$, then $(x_L, x_R) < (y_L, y_R)$.
3. For any $x_L, x_R, y_L, y_R$, if $x_L = y_L$ and $x_R < y_R$, then $(x_L, x_R) < (y_L, y_R)$.
4. For any $x, y$, $x < y$ if and only if one of the above conditions holds. Otherwise, write $x \not < y$.
Based on this, define “less than or equal to”: $x ≤ y \iff x < y$ or $x = y$. It is easy to see that:
1. $x ≤ y, y ≤ x ⇒ x = y$.
2. $x ≤ y, y ≤ z ⇒ x ≤ z$.
3. $x ≤ y$ or $y ≤ x$.
Further define:
1. $x > y \Longleftrightarrow y < x$.
2. $x ≥ y \Longleftrightarrow x \not < y$.
At this point, everything flourished and lived in harmony.
On the sixth day, because God had been so obsessed with arithmetic that he forgot to create nucleic acids and proteins, he could not create humans. But God was not willing to give up, so he waved his hand and said, “Let there be fleas,” and thus he molded a magical creature, the flea, out of mud.
God spent five days creating heaven and earth, and on the sixth day created the only life—fleas. Seeing that everything in the world was orderly and thriving, and that his flea was happily playing with mathematics, God was pleased and decided to make the seventh day a day of rest.
The flea’s daily life is very simple. At the beginning of a day, he takes an array $a[1,2,\cdots,n]$ of length $n$, initially all equal to $0$.
Then he repeatedly does one of the following two things:
1. He thinks of three positive integers $l, r, k$, then reassigns $a[k]$ to $(a[l], a[r])$. In particular, it is valid even if $l = k$ or $r = k$. This will not cause an error, because the flea always silently computes $(a[l], a[r])$ first, and then assigns it to $a[k]$.
It is guaranteed that $1 ≤ l, r, k ≤ n$.
2. He thinks of two positive integers $l, r$, then computes the maximum value among $a[l], a[l + 1], \cdots, a[r − 1], a[r]$.
It is guaranteed that $1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n$.
Of course, the flea knows how to do it. But he wants to test you.
Input Format
The first line contains two positive integers $n, m$, meaning an array of length $n$ and a total of $m$ operations. The next $m$ lines each describe an operation:
1. `C l r k`: Assignment operation, perform $a[k] = (a[l], a[r])$.
2. `Q l r`: Query operation, compute the maximum value among $a[l], a[l + 1], ..., a[r − 1], a[r]$. Output the index corresponding to the maximum value. If there are multiple maximum values, output the smallest index.
Output Format
For each query operation, output one line with the corresponding result.
Explanation/Hint
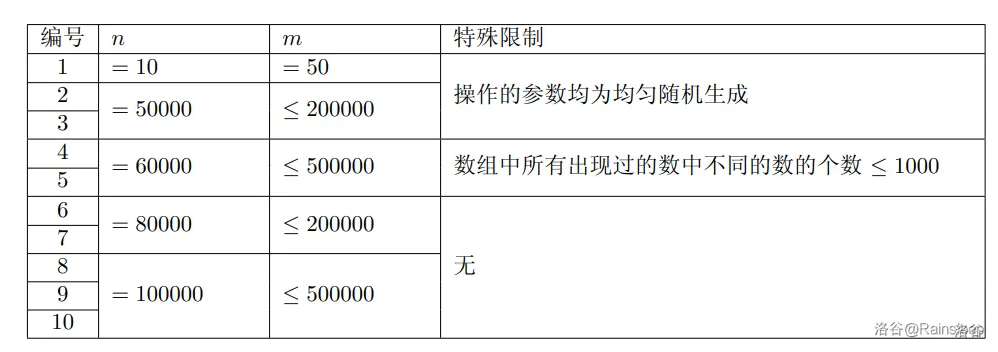
Translated by ChatGPT 5