P7268 [BalticOI 2000] Electronical Plate
Description
Given an $(n-1) \times (n-1)$ grid, each intersection point of two lines is a node, so the grid has $n \times n$ nodes. From left to right and from top to bottom, these nodes are numbered from $1$ to $n^2$ in order.
Some of these nodes are called “power sources”. Now we need to connect some wires, starting from power sources and going to other nodes. The wire must not pass through any other power source, and the endpoint must be a node on one of the four borders of the grid (top, bottom, left, or right).
For example, in the figure below, black nodes are power sources and white nodes are normal nodes:

Since some power sources are already on the border, we do not need to connect them. One feasible solution is:
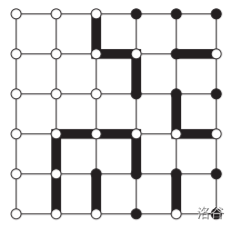
If there are multiple solutions, output any one of them.
Input Format
The first line contains an integer $n$, representing the size of the grid.
Then follow $n$ lines, each containing $n$ integers ($0$ or $1$), describing each node.
$0$ means this node is a normal node, and $1$ means this node is a power source.
Output Format
The first line contains an integer $k$, representing the minimum number of power sources that need to be connected with wires (power sources on the border do not need wires).
Then output $k$ lines. Each line starts with an integer, the number of the power source to be connected, followed by a string describing the route of the wire from that power source to the border: output `W` for left, `E` for right, `N` for up, and `S` for down. Power sources must be output in increasing order of their numbers.
If there are multiple solutions, output any one of them.
Explanation/Hint
#### Constraints
For $100\%$ of the testdata, $3 \le n \le 15$.
**This problem uses Special Judge.**
Thanks to the SPJ provider @[tiger2005](https://www.luogu.com.cn/user/60864).
#### Notes
Translated from [BalticOI 2000 Day1 C Electronical Plate](https://boi.cses.fi/files/boi2000_day1.pdf)。
Translated by ChatGPT 5