P9445 [ICPC 2021 WF] Mosaic Browsing
Description
The International Center for the Preservation of Ceramics (ICPC) is searching for motifs in some ancient mosaics. According to the ICPC's definition, a $\textit{mosaic}$ is a rectangular grid where each grid square contains a colored tile. A $\textit{motif}$ is similar to a mosaic but some of the grid squares can be empty. Figure G.1 shows an example motif and mosaic.
The rows of an $r_q \times c_q$ mosaic are numbered $1$ to $r_q$ from top to bottom, and the columns are numbered $1$ to $c_q$ from left to right.
A contiguous rectangular subgrid of the mosaic matches the motif if every tile of the motif matches the color of the corresponding tile of the subgrid. Formally, an $r_p \times c_p$ motif appears in an $r_q \times c_q$ mosaic at position ($r$, $c$) if for all $1 \leq i \leq r_p$, $1 \leq j \leq c_p$, the tile ($r+i-1$, $c+j-1$) exists in the mosaic and either the square ($i$, $j$) in the motif is empty or the tile at ($i$, $j$) in the motif has the same color as the tile at ($r+i-1$, $c+j-1$) in the mosaic.
Given the full motif and mosaic, find all occurrences of the motif in the mosaic.
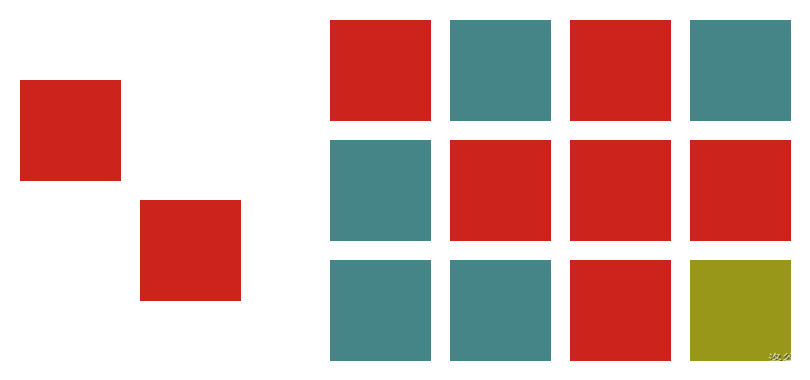
Figure G.1: Motif (left) and mosaic (right) of Sample Input 1.
Input Format
The first line of input contains two integers $r_p$ and $c_p$, where $r_p$ and $c_p$ ($1 \leq r_p, c_p \leq 1000$) are the number of rows and columns in the motif. Then $r_p$ lines follow, each with $c_p$ integers in the range $[0, 100]$, denoting the color of the motif at that position. A value of $0$ denotes an empty square.
The next line of input contains two integers $r_q$ and $c_q$ where $r_q$ and $c_q$ ($1 \leq r_q, c_q \leq 1000$) are the number of rows and columns in the mosaic. Then $r_q$ lines follow, each with $c_q$ integers in the range $[1, 100]$, denoting the color of the mosaic at that position.
Output Format
On the first line, output $k$, the total number of matches. Then output $k$ lines, each of the form $r c$ where $r$ is the row and $c$ is the column of the top left tile of the match. Sort matches by increasing $r$, breaking ties by increasing $c$.