P9558 [SDCPC 2023] Trie
Description
Recall the definition of a trie:
- A trie of size $n$ is a rooted tree with $n$ vertices and $(n - 1)$ edges, where each edge is marked with a character.
- Each vertex in a trie represents a string. Let $s(x)$ be the string vertex $x$ represents.
- The root of the trie represents an empty string. Let vertex $u$ be the parent of vertex $v$, and let $c$ be the character marked on the edge connecting vertex $u$ and $v$, we have $s(v) = s(u) + c$. Here $+$ indicates string concatenation, not the normal addition operation.
- The string each vertex represents is distinct.
We now present you a rooted tree with $(n + 1)$ vertices. The vertices are numbered $0, 1, \cdots, n$ and vertex $0$ is the root. There are $m$ key vertices in the tree where vertex $k_i$ is the $i$-th key vertex. It's guaranteed that all leaves are key vertices.
Please mark a lower-cased English letter on each edge so that the rooted tree changes into a trie of size $(n + 1)$. Let's consider the sequence $A = \{s(k_1), s(k_2), \cdots, s(k_m)\}$ consisting of all strings represented by the key vertices. Let $B = \{w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_m\}$ be the string sequence formed by sorting all strings in sequence $A$ from smallest to largest in lexicographic order. Please find a way to mark the edges so that sequence $B$ is minimized.
We say a string $P = p_1p_2\cdots p_x$ of length $x$ is lexicographically smaller than a string $Q = q_1q_2\cdots q_y$ of length $y$, if
- $x < y$ and for all $1 \le i \le x$ we have $p_i = q_i$, or
- there exists an integer $1 \le t \le \min(x, y)$ such that for all $1 \le i < t$ we have $p_i = q_i$, and $p_t < q_t$.
We say a string sequence $F = \{f_1, f_2, \cdots, f_m\}$ of length $m$ is smaller than a string sequence $G = \{g_1, g_2, \cdots, g_m\}$ of length $m$, if there exists an integer $1 \le t \le m$ such that for all $1 \le i < t$ we have $f_i = g_i$, and $f_t$ is lexicographically smaller than $g_t$.
Input Format
There are multiple test cases. The first line of th input contains an integer $T$ indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:
The first line contains two integers $n$ and $m$ ($1 \le m \le n \le 2 \times 10^5$) indicating the number of vertices other than the root and the number of key vertices.
The second line contains $n$ integers $a_1, a_2, \cdots, a_n$ ($0 \le a_i < i$) where $a_i$ is the parent of vertex $i$. It's guaranteed that each vertex has at most $26$ children.
The third line contains $m$ integers $k_1, k_2, \cdots, k_m$ ($1 \le k_i \le n$) where $k_i$ is the $i$-th key vertex. It's guaranteed that all leaves are key vertices, and all key vertices are distinct.
It's guaranteed that the sum of $n$ of all test cases will not exceed $2 \times 10^5$.
Output Format
For each test case output one line containing one answer string $c_1c_2\cdots c_n$ consisting of lower-cased English letters, where $c_i$ is the letter marked on the edge between $a_i$ and $i$. If there are multiple answers strings so that sequence $B$ is minimized, output the answer string with the smallest lexicographic order.
Explanation/Hint
The answer of the first sample test case is shown as follows.
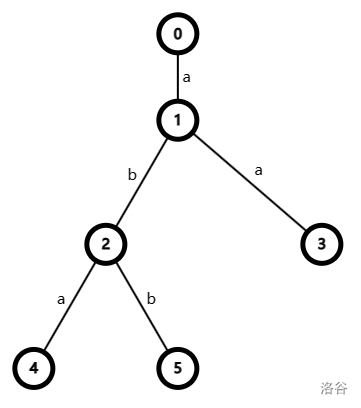
The string represented by vertex $1$ is ``a``. The string represented by vertex $4$ is ``aba``. The string represented by vertex $3$ is ``aa``. The string represented by vertex $5$ is ``abb``. So $B = \{$``a``, ``aa``, ``aba``, ``abb``$\}$.