P9568 [SDCPC 2023] Computational Geometry
Description
Given a convex polygon $P$ with $n$ vertices, you need to choose three vertices of $P$, denoted as $a$, $b$ and $c$ in counter-clockwise order. There must be exactly $k$ edges from $b$ to $c$ in counter-clockwise order (that is to say, $a$ is not an endpoint of these $k$ edges).
Consider cutting through $P$ with segment $ab$ and $ac$. Let $Q$ be the polygon consisting of $ab$, $ac$ and the $k$ edges between $b$ and $c$. It's easy to see that this polygon has $(k + 2)$ edges.
Find the maximum possible area of $Q$.
Note that $ab$ and $ac$ can overlap with edges of $P$.
Input Format
There are multiple test cases. The first line of the input contains an integer $T$ indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:
The first line contains two integers $n$ and $k$ ($3 \le n \le 10^5$, $1 \le k \le n-2$) indicating the number of vertices of the convex polygon $P$ and the number of edges from $b$ to $c$ in counter-clockwise order.
For the following $n$ lines, the $i$-th line contains two integers $x_i$ and $y_i$ ($-10^9 \le x_i, y_i \le 10^9$) indicating the $x$ and $y$ coordinate of the $i$-th vertex of the convex polygon $P$. Vertices are given in counter-clockwise order. It's guaranteed that the area of the convex polygon is positive, and there are no two vertices with the same coordinate. It's possible that three vertices lie on the same line.
It's guaranteed that the sum of $n$ of all test cases will not exceed $10^5$.
Output Format
For each test case output one line containing one real number indicating the maximum possible area of $Q$. Your answer will be considered correct if its relative or absolute error is less than $10^{-9}$.
Explanation/Hint
For the first sample test case, $Q$ is the whole triangle. Its area is $0.5$.
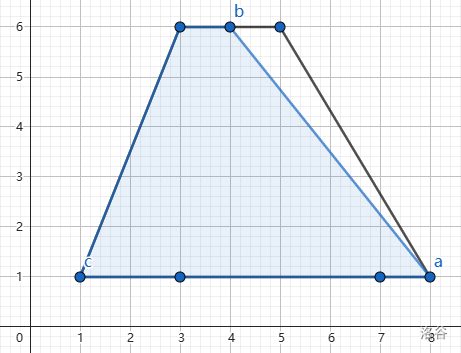
The second and third sample test case are shown below.