SP3495 NBLTHIEF - The Nobel Thief
Description
The Nobel Prize of Kabiguru Rabindranath Thagore was stolen from a museum of Viswa Bharati University in West Bengal. The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has been assigned the job to investigate the crime and recover the prize. CBI has identified some suspects and linked each one of them to a distinct subset of a set of clues.
Let there be _p_ suspects and _q_ clues. Integers 1 to _p_ identify suspects while _q_ distinct letter-codes identify clues. The clues are of varying importance. The alphabetic order of letter-codes determines the priority order in the clues; letter-codes 'a' to 'z' vary from highest to lowest priority.
Let _L_ $ _{0} $ be the set of all suspects. Based on a clue '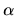', a subset _L_ of _L_ $ _{0} $ may be split into two disjoint subsets _L_ $ _{+} $ and _L_ $ _{-} $ . The subset _L_ $ _{+} $ includes all elements of _L_ that are linked to a subset of clues containing '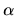' and _L_ $ _{-} $ includes all other elements of _L_. Let _n_, _n_ $ _{+} $ , and _n_ $ _{-} $ denote respectively the total number of elements in _L_, _L_ $ _{+} $ and _L_ $ _{-} $ . The discriminatory power of a clue '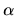' to discriminate suspects in _L_ is defined by 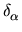 = - (| _n_ $ _{+} $ - _n_ $ _{-} $ |)
Let _L_ $ ^{*} $ denote a set of disjoint subsets of _L_ $ _{0} $ , each subset containing two or more elements. The discriminatory power 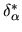 of a clue '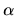' to discriminate suspects in subsets contained in _L_ $ ^{*} $ is defined to be the sum of all 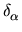's corresponding to each subset in _L_\*.
CBI wants to select a set _D_ of dominant clues so that the presence or absence of some or all of these clues can identify each suspect uniquely. The selection is to be done in stages.
Let _L_ $ ^{*} $ contain only _L_ $ _{0} $ initially. At each stage of selection a clue '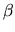' with highest discriminatory power 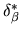 is selected. Selecting the clue '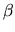' with highest priority breaks tie, if any. After a selection of '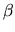' each _L_ in _L_ $ ^{*} $ is split into disjoint subsets _L_ $ _{+} $ and ' _L_ $ _{-} $ ' all resulting subsets with less than two elements are dropped from _L_ $ ^{*} $ . The process of selection continues until _L_ $ ^{*} $ becomes empty. All the clues thus selected form the set of dominant clues _D_.
You are required to write a program to find the set of dominant clues _D_.
Input
----------------------------------------------------
Input may contain multiple test cases. For each test case input is given in one line. It contains an integer _k_ representing the case number and a certain number of strings of clues. The _i_-th string represents the subset of clues to which the _i_-th suspect is linked. A space separates two consecutive fields in input.
Input terminates with an input 0 for the case number _k_.
Output
-----------------------------------------------------
For each test case, present output in one line. The line contains the case number _k_ and a string of letters. The letters in the string correspond to the clues in _D_ and appear in the order of their selection.
Sample Input
-----------------------------------------------------------
```
1 cbx cpxb bc brc
2 bac adce cbd d
0
```
Sample Output
------------------------------------------------------------
```
1 xpr
2 ab
```
- - - - - -
Kanpur-Kolkata 2004-2005
Input Format
N/A
Output Format
N/A