SP7192 INTEGMAX - Integral Maximization
Description
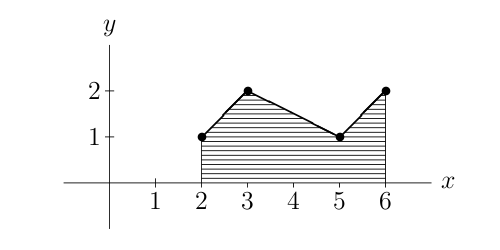
A set of points on the XY plane, all of them with different x coordinate, defines a polygonal
line in the following way: sort the points in increasing order of their x coordinates, and connect
each point with its neighbors. The integral of such polygonal line is the area contained below
the line and above the x axis, between the first and last values of x. For instance, the set of
points {(5, 1), (3, 2), (6, 2), (2, 1)} defines the polygonal line shown in the figure; the integral of
the polygonal line is the shaded area, with a value of 6.
Given a set of N different values for x, and a set of N values for y, we want to pair them to
form N points on the plane such that the integral of the polygonal line defined by the points is
as large as possible.
Input Format
The input contains several test cases, each one described in exactly three lines. The first line of
each test case contains an integer N indicating the number of points in the set (2 The second line contains N different integers Xi separated by single spaces (1 for 1 (Xi < Xi+1 for 1 (1 particular order. The last line of the input contains a single −1 and should not be processed
as a test case.
Output Format
For each test case output a single line with the maximum integral of a polygonal line formed
by pairing the input values, using exactly one decimal digit. Notice that one decimal digit is
always enough to represent the exact value of the integral of a polygonal line defined by points
with integer coordinates.