最近公共祖先
jesse1216
·
·
算法·理论
最近公共祖先
简介
最近公共祖先,英文名 \text{Lowest Common Ancestor},被简记为 \text{LCA}。
举例:如下图,$\text{LCA}(7,8)=4$,$\text{LCA}(5,9)=1$。
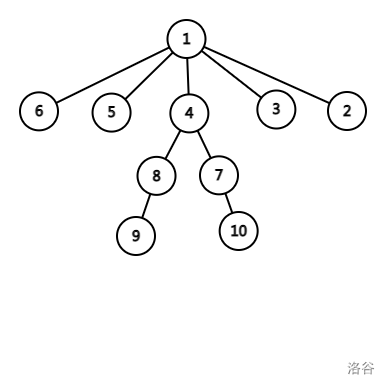
本文将分别介绍两种方法求最近公共祖先,这两种方法各有所长,希望大家都能掌握。
## 前置知识
在学习最近公共祖先之前,请你掌握以下知识点:
- 树的基本操作;
- [$\text{ST}$ 表及 $\text{RMQ}$](https://www.luogu.com.cn/article/rmxl5va7);
- [链式前向星](https://www.luogu.com.cn/article/8fsxpdo6)。
## 说明
- 定义 $dep_x$ 为结点 $x$ 的深度(根结点的深度为 $1$);
- 定义 $fa_x$ 为结点 $x$ 的父亲(根结点的父亲为 $0$)。
- 定义树上两点 $x$、$y$ 的距离为 $Dis(x,y)$;
## 算法介绍
### $1.$ 暴力法
我们采用“向上跳跃”的方法寻找 $\text{LCA}$。
重复执行以下操作,直到 $x=y$:
- 令 $x$ 和 $y$ 中深度较大者变为其父亲(如果深度相同,则同时变为自己的父亲)。
$x=y$ 时该结点即为 $\text{LCA}(x,y)$。单次查询时间复杂度 $O(n)$。
#### 暴力法代码
```cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 5;
int n, m, s, x, y;
int f[N], dep[N];
vector<int> v[N];
void dfs(int x, int fa) {
f[x] = fa, dep[x] = dep[fa] + 1;
for (int i : v[x])
if (i != fa)
dfs(i, x);
}
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m >> s;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
cin >> x >> y;
v[x].push_back(y), v[y].push_back(x);
}
dfs(s, 0);
while (m--) {
cin >> x >> y;
while (x != y) {
if (dep[x] < dep[y]) y = f[y];
else if (dep[x] == dep[y]) x = f[x], y = f[y];
else x = f[x];
}
cout << x << endl;
}
return 0;
}
```
### $2.$ 倍增法
> $1.$ 把 $x$ 与 $y$ 中深度较大者向上跳,使得两个结点在同一深度。
> $2.$ 把 $x$ 和 $y$ 同时向上跳。
这是暴力做法的另一种叙述方式。我们考虑优化这一算法。
#### 优化求一个结点的所有祖先的算法
>
> 求出 $x$ 的祖先可以使用 $\text{ST}$ 表。
> 具体的,记 $f(x,i)$ 为 $x$ 的 $2^i$ 阶祖先,则 $f$ 的递推式为:
> $$f(x,i)=\begin{cases}fa_x,i=0\\f(f(x,i-1),i-1),i\not=0\end{cases}$$
> 这样,把 $k$ 转为二进制,$x$ 的 $k$ 阶祖先就可以 $O(\log n)$ 求出。
暴力算法有两个步骤,依次优化:
- 第一步:把 $x$ 与 $y$ 中深度较大者向上跳,使得两个结点在同一深度。
> 不妨设 $dep_x\ge dep_y$,则令 $x$ 向上跳 $dep_x-dep_y$ 次即可。
>
> 首先将 $dep_x-dep_y$ 转为二进制,若其第 $p$ 位为 $1$,则将 $x$ 向上跳 $2^p$ 次,即变为 $f(x,p)$。我们将这些程序写成一个函数 $Jump(x,k)$,表示求 $x$ 的 $k$ 阶祖先。
>
> 时间复杂度为 $O(\log n)$。
- 第二步:把 $x$ 和 $y$ 同时向上跳。
> 可以二分向上跳跃的次数 $len$,找到最小的 $len$ 使得 $Jump(x,len)=Jump(y,len)$,二分时间复杂度 $O(\log n)$,而 $Jump$ 函数也需要 $O(\log n)$,时间复杂度 $O((\log n)^2)$。
>
> 思考:这个二分是否有必要?答案是否定的。
>
> 我们只需模仿第一步枚举向上跳的层数即可,具体的,枚举 $p\in[0,\log n]$,验证 $f(x,p)$ 是否与 $f(y,p)$ 相等,如果不是,那么我们将 $x$ 和 $y$ 同时向上跳 $2^p$ 次;否则不改变 $x$ 和 $y$,因为我们并不确定该公共祖先是否为最近的。最后求得的 $x$ 为 $\text{LCA}(x,y)$ **的儿子**。代码时间复杂度为 $O(\log n)$。
#### 注意
在第一步执行完后,若有 $x=y$,则立即返回 $\text{LCA}(x,y)=x$,否则将在第二步中返回 $\text{LCA}(x,y)=fa_x$,导致错误。
#### 倍增法复杂度
- 时间复杂度: 预处理 $O(n\log n)$,单次查询 $O(\log n)$。
- 空间复杂度:$\text{ST}$ 表 $O(n\log n)$。
#### 倍增法代码
```cpp
#include <stdio.h>
const int N = 5e5 + 5;
int n, T, s, a, b, f[N][20], dep[N];
int cnt, head[N], to[N << 1], nxt[N << 1];
inline void read(int &x) {
x = 0;
char c = getchar();
while (c < '0' || c > '9') c = getchar();
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48), c = getchar();
}
inline void write(const int &x) {
if (x >= 10) write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
inline void Add(int x, int y) {
cnt++;
to[cnt] = y, nxt[cnt] = head[x], head[x] = cnt;
}
void dfs(int x, int fa) {
f[x][0] = fa, dep[x] = dep[fa] + 1;
for (int i = head[x]; i != 0; i = nxt[i]) if (to[i] != fa) dfs(to[i], x);
}
inline void Init(void) {
dfs(s, 0);
for (int i = 1; (1 << i) <= n; i++)
for (int x = 1; x <= n; x++)
f[x][i] = f[f[x][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
inline void Jump(int &x, int len) {
for (int p = 19; p >= 0; p--)
if (len >= (1 << p))
x = f[x][p], len -= (1 << p);
}
inline int LCA(int x, int y) {
if (dep[x] < dep[y]) x ^= y ^= x ^= y; // swap(x, y)
Jump(x, dep[x] - dep[y]);
if (x == y) return x;
for (int p = 19; p >= 0; p--)
if (f[x][p] != f[y][p])
x = f[x][p], y = f[y][p];
return f[x][0];
}
int main(void) {
read(n), read(T), read(s);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
read(a), read(b);
Add(a, b), Add(b, a);
}
Init();
while (T--) {
read(a), read(b);
write(LCA(a, b)); putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
```
### $3.$ 欧拉序列
#### 引入
我们将题目数据加强,令结点数目 $n\le10^6$,查询次数 $m\le10^7$。
这道加强版的题目中,单次查询复杂度需要降低至 $O(1)$,而倍增法单次查询复杂度为 $O(\log n)$,无法通过。
于是我们需要另一种能 $O(1)$ 查询的算法。
#### 树的欧拉序列
在每次进入结点(无论是遍历还是回溯)时将编号加入序列,就得到了树的欧拉序列。
例如以下这一棵树的欧拉序列为 $\{2,6,1,6,5,6,4,6,2,3,7,3,8,3,2\}$。
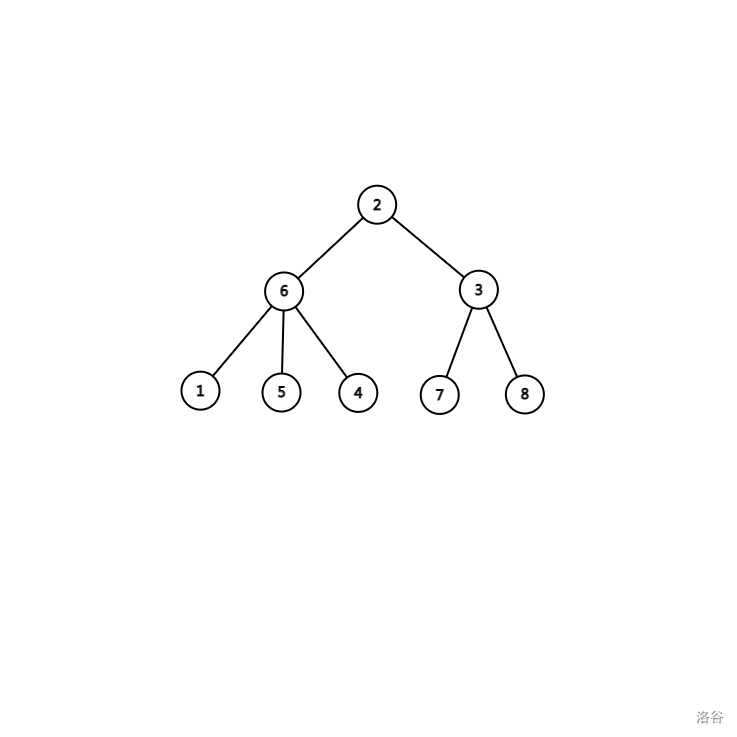
可以发现,树的欧拉序列的长度必为 $2\times n-1$。
欧拉序列会将树的父子关系(从属关系)转为嵌套的区间。
#### 欧拉序列求解 $\text{LCA}
在欧拉序列上,一个路径被转为欧拉序列的一个子序列,例如下图中 5 至 7 的路径转为序列 \{5,6,4,6,2,3,7\},这段序列的两个端点恰为 5 和 7 第一次出现的位置。
记 id_x 为 x 在欧拉序列中第一出现的位置。则上图中 id 序列为 \{3,1,10,7,5,2,11,13\}
可以发现 \text{LCA}(x,y) 是在欧拉序列中从 id_x 到 id_y 的路径上深度最小的那个结点。而深度最小的结点可以通过 \text{ST} 表进行维护。定义 p(i,j) 为欧拉序中第 i 个点至第 i+2^j-1 个点中深度最小的结点编号,于是 p(i,j) 的递推公式如下:
p(i,j)=
\begin{cases}
i & j=0\\
Better\left(p(i,j-1),p(i+2^{j-1},j-1)\right) & j\not=0
\end{cases}
其中 Better(x,y) 为 x 和 y 中深度较小的点的编号。
欧拉序解法复杂度
- 时间复杂度: 预处理 O(n\log n),单次查询 O(1)。
- 空间复杂度:\text{ST} 表 O(n\log n)。
欧拉序解法代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
inline void read(int &x) {
x = 0;
char c = getchar();
while (c < '0' || c > '9') c = getchar();
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48), c = getchar();
}
inline void write(const int &x) {
if (x >= 10) write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
const int N = 5e5 + 5;
int n, m, s, x, y, cnt, p[N << 1][22], dep[N], id[N];
int tot, head[N], to[N << 1], nxt[N << 1];
inline void add(int x, int y) {
tot++, to[tot] = y, nxt[tot] = head[x], head[x] = tot;
}
void dfs(const int &x, const int &fa) {
dep[x] = dep[fa] + 1, p[++cnt][0] = x, id[x] = cnt;
for (int i = head[x]; i != 0; i = nxt[i]) if (to[i] != fa) {
dfs(to[i], x);
p[++cnt][0] = x;
}
}
inline int Updateid(const int &x, const int &y) {
return (dep[x] < dep[y]) ? x : y;
}
inline int LCA(int l, int r) {
l = id[l], r = id[r];
if (l > r) swap(l, r);
int tmp = log2(r - l + 1);
return Updateid(p[l][tmp], p[r - (1 << tmp) + 1][tmp]);
}
int main(void) {
read(n), read(m), read(s);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
read(x), read(y);
add(x, y), add(y, x);
}
dfs(s, 0);
for (int j = 1; (1 << j) <= cnt; j++)
for (int i = 1; i + (1 << j - 1) - 1 <= cnt; i++)
p[i][j] = Updateid(p[i][j - 1], p[i + (1 << j - 1)][j - 1]);
while (m--) {
read(x), read(y);
write(LCA(x, y)); putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
4. 总结
我们学习了两种算法,分别为倍增法和欧拉序解法,两种解法各有所长:
- 倍增法的优势在于好写、常数小,然而单次查询复杂度为 O(\log n),无法通过查询次数较大的题目。
- 欧拉序解法胜于单次查询复杂度为 O(1),而劣势在于预处理的常数较大。
\text{LCA} 的应用
最近公共祖先是一个较为基础的算法,很多图论题目中都需要用到。
举例
\text{Problem }1. 求解树上任意两点的距离
回顾区间求和,我们使用了前缀和解决。在树上,我们仍然可以使用前缀和:令 $sum_x$ 为根结点至 $x$ 的路径长度,则递推式为 $sum_x=sum(fa_x)+(fa_x$ 至 $x$ 的边的边权 $)$。
于是,$x$ 到 $\text{LCA}(x,y)$ 的路径长度为 $sum_x-sum_{\text{LCA}(x,y)}$,可以 $O(1)$ 算出。$y$ 到 $\text{LCA}(x,y)$ 同理。
最后得出:$x$ 至 $y$ 的路径长度为 $sum_x+sum_y-2\cdot sum_{\text{LCA}(x,y)}$。
在无权树上,$sum_x=dep_x$。
#### $\text{Problem }2.$ 计算到给定的三个点距离之和最小值
设 $s$ 为到 $a$、$b$、$c$ 三点距离和最近的结点。此时到三个点的距离之和为 $sum=Dis(a,s)+Dis(b,s)+Dis(c,s)$,让此式最小,相当于让 $2\cdot sum=(Dis(a,s)+Dis(s,b))+(Dis(b,s)+Dis(s,c))+(Dis(c,s)+Dis(s,a))$ 最小。
易得 $\begin{cases}Dis(a,s)+Dis(s,b)\ge Dis(a,b)\\Dis(b,s)+Dis(s,c)\ge Dis(b,c)\\Dis(c,s)+Dis(s,a)\ge Dis(c,a)\end{cases}$。
相加得 $2\cdot sum\ge Dis(a,b)+Dis(b,c)+Dis(c,a)$,即 $sum\ge\frac{Dis(a,b)+Dis(b,c)+Dis(c,a)}{2}$。
取等时 $t$ 同时在路径 $\overline{ab},\overline{bc},\overline{ca}$ 上。
构造:一定可以找到满足条件的 $t$。
- 情况 $(1)$:
- 情况 $(2)$:
- 情况 $(3)$:
故答案为 $\frac{Dis(a,b)+Dis(b,c)+Dis(c,a)}{2}$。
#### $\text{Problem }3.$ 统计有多少个点到两点的距离相等
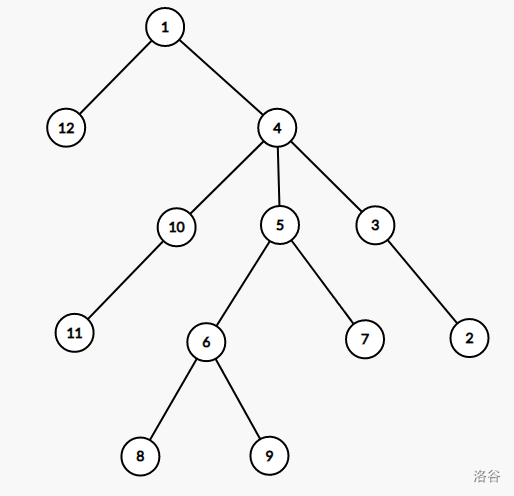
按 $a$ 和 $b$ 的位置关系分类讨论(记 $Dis(a,b)=len$):
- $a=b$,如 $x=y=7$:
答案为 $n$,显然所有的结点均满足条件。
- $len$ 为奇数,如 $x=3,y=11$:
答案为 $0$,由于距离为奇数,故不存在某个点至两点距离相等。
- $dep_a=dep_b$,如 $x=2,y=11$:
设 $a_0=Jump(a,\frac{len}{2}-1)$,$b_0=Jump(b,\frac{len}{2}-1)$,则答案为不在 $a_0$ 且不在 $b_0$ 的子树上的所有点。
- $dep_a\not=dep_b$,不妨设 $dep_a<dep_b$,如 $x=10,y=8$:
设 $k=Jump(b,\frac{len}{2})$(显然 $k$ 为 $\overline{ab}$ 的中点),$b_0=Jump(b,\frac{len}{2}-1)$,则答案为所有在 $k$ 的子树中且不在 $b_0$ 的子树中的所有点。
## 练习
- [P3379 【模板】最近公共祖先](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3379)
- [P3398 仓鼠找 sugar](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3398)
- [P4281 紧急集合 / 聚会](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4281)
- [P2597 灾难](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2597)
- [P1852 跳跳棋](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1852)
- [U292899 最近公共祖先](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/U292899)
#### 【提示】
- 请用两种方法分别完成第一题,练习基本功。
- 第二、三题为 $\text{LCA}$ 的基本应用。
- 第四题为求解 $\text{DAG}$(有向无环图)的支配树问题。
支配树是每个点直接连向其必经点的树形结构,例如左下图 $\text{DAG}$ 的支配树如右下图。
对于点 $x$,设它的入边为 $(y_1,x),(y_2,x),\dots,(y_t,x)$,则 $x$ 在支配树中的父亲是 $\text{LCA}(y_1,y_2,\dots,y_t)$。在支配树中加入结点时需要按照拓扑序。
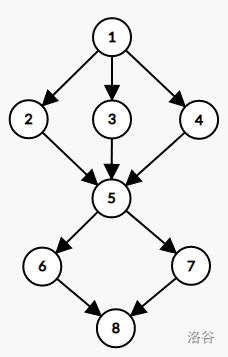 $\text{ }$ 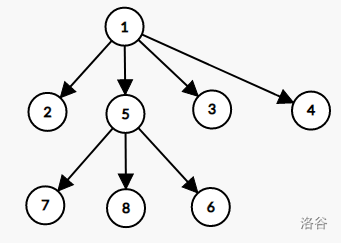
- 第五题是复杂建模问题,比较困难,请读者自己思考。可以参考[这一篇博客](https://www.luogu.com.cn/article/s4k6yxmb)。